Learning Data Structures and Algorithms can feel confusing when you do not know where to start. Many learners struggle because they study topics randomly without a clear plan. A well-structured roadmap helps you move step by step, avoid confusion, and focus on the right concepts at the right time.
This DSA Roadmap 2026 is designed to guide you from basic programming to advanced problem-solving skills. This DSA roadmap for beginners helps you to know how to build strong logic, practice consistently, and prepare confidently for coding interviews and competitive programming in a simple and effective way.
What are Data Structures and Algorithms?
Data Structures and Algorithms are core concepts used to solve problems in programming. A data structure is a way to store, organize, and manage data so it can be accessed and used easily. Examples include arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, and graphs. Algorithms are step-by-step procedures used to perform operations on data or solve specific problems. Together, they help programmers handle data logically, improve problem-solving skills, and build applications that work smoothly with both small and large amounts of data.
Why Data Structures and Algorithms Matter
Data Structures and Algorithms help us solve problems in a faster and smarter way. Below, we will explain why they matter and how they support problem-solving, performance, interviews, and real-world development.
1. Efficient Problem Solving
Data structures and algorithms allow you to break complex problems into smaller parts. This helps you design clear solutions, avoid unnecessary steps, and handle large inputs efficiently without slowing down your program.
2. Better Performance and Optimization
Using the right data structure and algorithm improves speed and memory usage. Your code runs faster, handles larger data smoothly, and works well in real-world applications and competitive coding scenarios.
3. Strong Foundation for Coding Interviews
Most technical interviews focus on data structures and algorithms. Knowing them helps you answer questions confidently, explain your logic clearly, and solve problems within time limits during interviews.
4. Real-World Application Development
Data structures and algorithms are used in real systems like search engines, databases, and apps. They help you write clean, maintainable code that works efficiently as applications grow.
Why DSA is Required in Top Tech Jobs
Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) are required in top tech jobs because they help you write efficient, scalable, and optimized code. Companies look for engineers who can solve complex problems, handle large data, and choose the best approach under constraints. Strong DSA skills show your logical thinking, problem-solving ability, and coding depth, which is why they are heavily tested in technical interviews and real-world software development roles.
Recommended Professional Certificates
Full Stack Development Mentorship Program
WordPress Bootcamp
DSA Roadmap 2026: A Step-by-Step Learning Guide
This DSA roadmap step by step provides a clear learning path from start to end. Below are the key steps you should follow to build strong fundamentals and progress confidently in your DSA journey.
- Begin Your DSA Journey with One Programming Language
- Learn About Time and Space Complexities
- Learn Core Data Structures and Algorithms
- Practice Consistently and Build Problem-Solving Skills
- Compete, Analyze, and Become Interview-Ready
Next, we will go through each step one by one to clearly explain what you should learn, how to practice effectively, and how to progress confidently in your DSA learning journey.
Step 1: Begin Your DSA Journey with One Programming Language
The first step is to get started with a programming language you are comfortable with. Focus on learning basics such as variables, data types, loops, functions, and conditionals. A strong foundation in one language helps you understand DSA concepts clearly and avoid confusion while solving problems. Stick to one language before moving to advanced topics.
Language-Specific Prerequisites:
- C Language: C Variables, C Loops, C Control Statements, C Functions, C Pointers & C Dynamic Memory Allocation, C Structures, C Unions
- C++ Language: C++ Variables, C++ Data Types, C++ Loops, C++ Control Statements, C++ Functions, C++ Arrays, C++ Pointers, C++ References, C++ Basic OOP Concepts
- Python: Python Variables, Python Data Types, Python Loops, Python Conditional Statements, Python Functions, Python Lists, Python Tuples, Python Dictionaries, Python Sets, Python Basic Recursion
- Java: Java Variables, Java Data Types, Java Loops, Java Conditional Statements, Java Methods, Java Arrays, Java Classes & Objects, Java OOP Concepts
- JavaScript: JS Variables and Constants, JS Data Types, JS Loops, JS Conditional Statements, JS Functions, JS Arrays, JS Objects, JS Basic Recursion
Step 2: Learn About Time and Space Complexities
The next step is to understand time and space complexity, which help you measure how efficient your code is. Time complexity explains how an algorithm’s execution time increases with input size, while space complexity shows memory usage. Learning these concepts helps you choose better solutions, optimize performance, and handle large datasets confidently during coding interviews and real-world applications.
It includes many different notations such as:
- Big O Notation – O()
- Omega Notation – Ω()
- Theta Notation – Θ()
For more detailed explanations, you can also check out:
Step 3: Learn Core Data Structures and Algorithms
The next step is to learn core data structures and algorithms, which are the backbone of efficient problem-solving. You need to understand how data is stored, organized, and processed in different ways. Concepts like arrays, strings, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs, and common algorithms help you solve problems effectively. Learning these topics improves your logical thinking, helps you choose the right approach, and prepares you for coding interviews, competitive programming, and real-world software development.
3.1 Arrays
An array data structure is one of the most basic and commonly used data structures in DSA. It allows you to store multiple values of the same data type in a single variable with a fixed size. Because elements are stored in continuous memory locations, arrays allow fast and direct access using index positions, making them efficient for reading and processing data.

Each element in an array is accessed using an index that begins at 0 and increases sequentially. For example, an array containing six elements uses index positions from 0 to 5. Arrays are commonly used to store numbers, strings, and objects, making data access and processing simple and organized in real-world programs.
3.2 Multidimensional Arrays
A multidimensional array stores data in more than one dimension, such as rows and columns. It is commonly used to represent tables, matrices, or grid-based data where values need to be organized in a structured format.
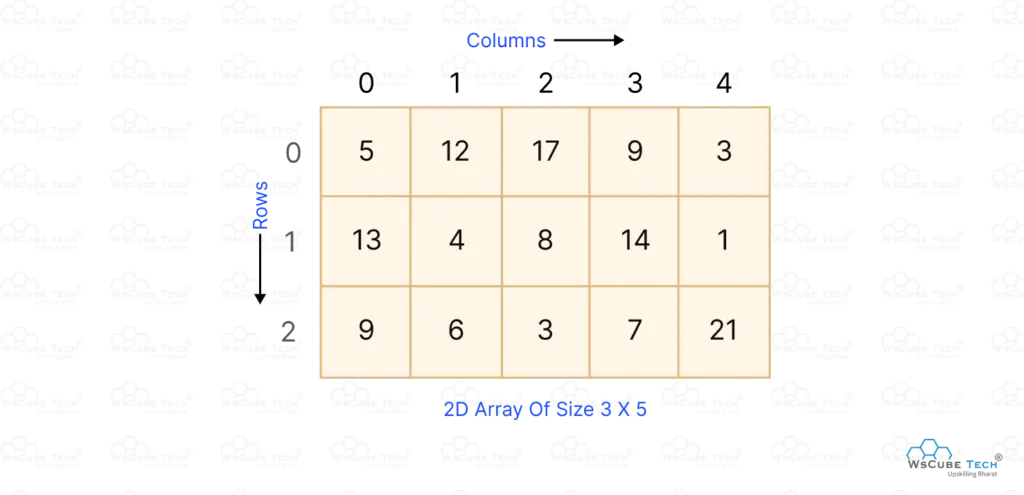
In this diagram, the multidimensional array stores data in a table format with 3 rows and 5 columns, making it simple to access, update, and manage related values.
3.3 Strings
A string is a sequence of characters used to store and work with text data. It is commonly used for handling names, words, sentences, and user input in programs. Strings allow easy access to individual characters using index positions and support common operations like searching, updating, and comparing text.
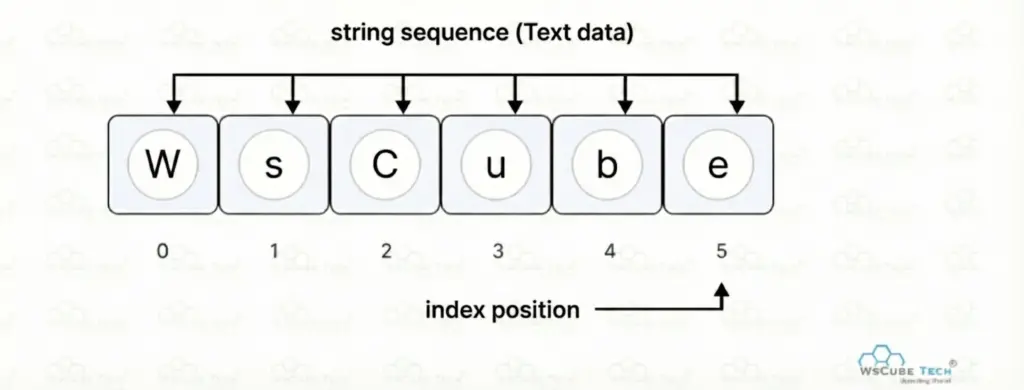
In the string “WsCube”, characters are stored individually as W, s, C, u, b, and e. Each character has an index position starting from 0 to 5, which allows fast, direct, and easy access during string operations.
3.4 Recursion and Backtracking
Recursion is a programming technique where a function calls itself to solve a problem by breaking it into smaller subproblems. It is useful for problems that have a repeating structure, such as tree traversal, factorial calculation, and searching tasks.
Backtracking is an extension of recursion used to explore multiple possible solutions. It tries one option at a time and backtracks when a solution fails, making it useful for problems like puzzles, permutations, and combinations. Some important topics related to this section that are essential for placements include:
3.5 Sorting Algorithms
Sorting algorithms are used to arrange data in a specific order, such as ascending or descending. They help make searching, comparison, and data processing faster and more efficient. Learning sorting algorithms improves your understanding of time complexity and helps you choose the best approach based on problem size.
Below are some important sorting techniques you should know to understand data organization, improve efficiency, and choose the right algorithm based on problem size and requirements:
3.6 Linked List
A linked list is a dynamic linear data structure made up of nodes. Each node contains two parts: one to store data and another to store the address of the next node. Unlike arrays, linked lists do not store elements in continuous memory locations, which allows flexible memory usage and easy insertion or deletion of elements.
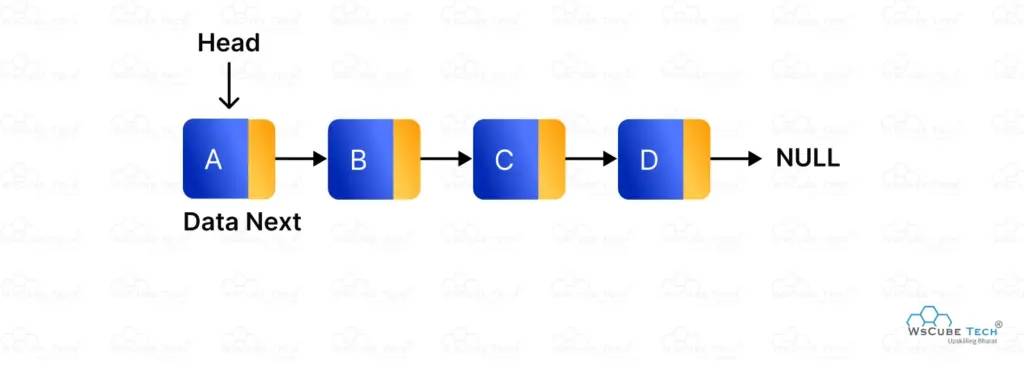
The first node of a linked list is called the head, and it points to the next node in the sequence. Each node links to the following node until the last one, which points to null. Linked lists are mainly of three types: singly linked list, doubly linked list, and circular linked list, each serving different use cases.
Upcoming Masterclass
Attend our live classes led by experienced and desiccated instructors of Wscube Tech.
3.7 Stacks
Stacks and queues are basic linear data structures used to manage data in an ordered manner. A stack follows the Last In, First Out (LIFO) rule, where the most recently added element is removed first. In a stack, we perform two main operations: push, which adds an element to the top, and pop, which removes the top element.
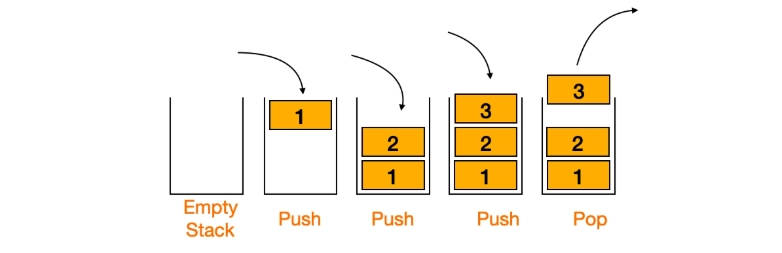
In this example, the visual shows an empty stack where elements 1, 2, and 3 are pushed sequentially. When a pop operation is performed, 3 is removed first, clearly showing the LIFO rule.
3.8 Queues
Queues are linear data structures that follow the First In, First Out (FIFO) rule, meaning the element added first is removed first. A queue has two ends: the front, where elements are removed, and the rear, where new elements are added.
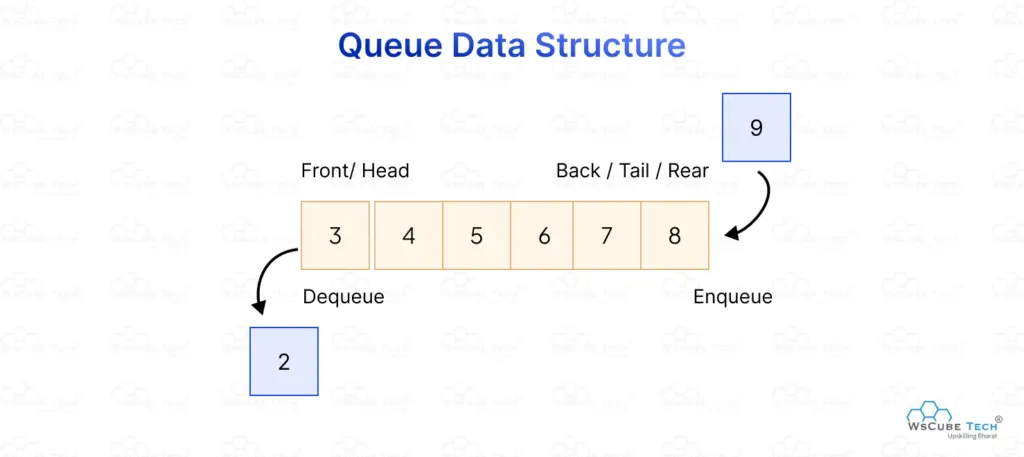
In this example, the queue contains the elements 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8, where 2 is at the front. When a dequeue operation is performed, 2 is removed first. After that, an enqueue operation adds 9 at the rear of the queue, maintaining the FIFO order.
3.9 Binary Search Trees
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a tree-based data structure where each node has at most two children. In a BST, values smaller than the parent are stored on the left, and larger values are stored on the right. This ordered structure makes operations like searching, inserting, and deleting data faster and more organized. BSTs are commonly used to manage sorted data efficiently.
3.10 Heaps and Priority Queues
Heaps and priority queues are special tree-based data structures used to manage data based on priority. A heap keeps elements organized so that the highest or lowest value is always at the top. Priority queues use this property to process elements according to importance, not insertion order. They are commonly used in scheduling, pathfinding algorithms, and task management systems.
3.11 Graphs and Graph Traversals
Graphs are data structures that show how different nodes are connected and how they relate to each other. They consist of vertices (nodes) connected by edges and are commonly used to model networks such as social media, maps, and communication systems. Graphs can be directed or undirected, depending on how connections flow between nodes.
Graph traversal is the process of visiting all nodes in a graph in a systematic way. Common traversal techniques include Depth First Search (DFS) and Breadth First Search (BFS), which help explore paths, detect cycles, and analyze connections efficiently.
3.12 Dynamic Programming
Dynamic Programming is a problem-solving approach used to handle complex problems by dividing them into smaller, related subproblems. Instead of solving the same problem repeatedly, it saves previous results and reuses them when needed. This reduces unnecessary calculations and improves overall performance. Dynamic programming is commonly applied in optimization tasks, sequence-based problems, and situations where finding the best possible result through planned decisions is required.
Step 4: Practice Consistently and Build Problem-Solving Skills
Consistent practice is the key to mastering DSA concepts and improving logical thinking. Solving problems regularly helps you understand patterns, optimize solutions, and gain confidence. Following a data structures and algorithms roadmap keeps your practice structured and goal-focused. You can strengthen your skills further by solving real problems on WsCube Code Challenges, where hands-on practice helps you apply concepts effectively for interviews and real-world scenarios.
Step 5: Compete, Analyze, and Become Interview-Ready
Participating in coding competitions helps you improve speed, accuracy, and confidence under time pressure. Analyzing your solutions and mistakes is equally important, as it helps you identify weak areas and improve your approach. Regular practice, mock interviews, and reviewing problem patterns prepare you to perform confidently in technical interviews and real-world coding challenges.
Career Opportunities After Learning DSA
Learning DSA strengthens problem-solving skills and opens many career paths in technology. Below are the career opportunities you can pursue if you follow a structured DSA learning roadmap and practice consistently.
Core Tech Roles
- Software Developer – Uses DSA to write clean, optimized code, solve complex programming problems, and improve application performance in real-world software projects across different domains.
- Backend Engineer – Uses DSA to manage data, design fast APIs, and handle high user traffic. Strong DSA knowledge helps reduce delays, prevent performance problems, and build stable, reliable server-side systems for real-world applications.
- System Engineer – Uses DSA to design scalable systems, manage resources properly, and keep applications stable, fast, and reliable even when handling heavy workloads.
Explore More Web Development Blog Topics
| Web Design Vs Web Development | Java vs JavaScript |
| Magento Vs WooCommerce | HTML Vs HTML5 |
| Frontend Vs Backend Development | Coding Vs Programming |
Specialized Fields
- Data Engineer – Uses DSA to handle large datasets, build structured data pipelines, reduce processing delays, and support data-driven systems. Strong DSA skills help manage data flow, improve performance, and scale platforms smoothly as data volume grows.
- Machine Learning Engineer – Applies DSA concepts to handle large training data, optimize algorithms, and improve model performance in production-level machine learning systems.
- Competitive Programmer – Uses strong DSA skills to solve complex problems quickly, manage time limits, and perform confidently in coding contests and technical interviews.
Best DSA Learning Tips for Working Professionals
Following a clear DSA roadmap helps working professionals learn DSA step by step, manage time better, stay consistent, and prepare effectively for interviews without affecting daily work responsibilities.
- Set Clear Daily Goals: Create small, achievable daily goals instead of long study sessions. This helps you stay consistent, reduce stress, and make steady progress even with a busy work schedule.
- Focus on One Topic at a Time: Avoid learning multiple topics together. Concentrate on one data structure or algorithm, understand it clearly, and practice related problems before moving to the next concept.
- Practice Smart, Not More: Solve quality problems instead of many random ones. Focus on understanding patterns, improving logic, and analyzing mistakes to strengthen problem-solving skills effectively.
- Use Weekends for Revision: Utilize weekends to revise previously learned topics, re-solve problems, and clear doubts. Regular revision helps retain concepts and boosts confidence over time.
- Track Progress and Weak Areas: Maintain a simple tracker to record completed topics and identify weak areas. Regularly revisiting these weak points helps you improve accuracy, strengthen understanding, and perform better during technical interviews and problem-solving practice.

How WsCube Tech Helps You Master DSA
WsCube Tech provides a structured and beginner-friendly way to learn DSA from scratch. You can follow clear DSA tutorials that explain concepts step by step in simple language. Along with learning, you can practice important DSA interview questions that help you understand problem patterns and prepare confidently for technical interviews.
To support hands-on learning, WsCube Tech also offers an online compiler where you can try code instantly. You can practice DSA using Our C Examples, C++ Examples, Python Examples, Java Examples, and JavaScript Examples, without any setup. This practical approach helps you test logic quickly, fix mistakes, and strengthen problem-solving skills effectively. By following this complete DSA roadmap, you can learn step by step, practice regularly, and build strong problem-solving skills in a simple and effective way.
DSA Roadmap (Video Guide)
FAQs About DSA Roadmap
Data structures help you store data in an organized way, and algorithms are step-by-step methods you use to solve problems and work with that data easily.
DSA is not difficult for beginners if you start slowly and follow a structured roadmap. With simple explanations, regular practice, and patience, you can easily understand concepts and build confidence step by step.
The time depends on your consistency and background. You can complete a DSA learning roadmap in six to nine months with regular practice, clear concepts, and focused problem-solving sessions.
You can choose C++, Java, or Python for DSA. The best language is the one you are comfortable with, because logic, consistency, and problem-solving matter more than the programming language itself.
Yes, working professionals can follow the DSA roadmap 2026 by studying daily for short durations. Consistent practice, smart topic selection, and focused revision help you balance work and learning.
Yes, the DSA roadmap helps you write better code, handle large data, and solve real-world problems. Strong DSA skills improve application performance and make you a better software developer overall.
DSA is not mandatory for DevOps roles, but it helps you understand system logic, optimize scripts, solve problems faster, and perform better in interviews, especially for DevOps engineers in product-based companies.
You should practice DSA daily or regularly to see progress. Solving problems consistently for several months helps you understand patterns, improve speed, and become confident in interviews and real-world coding.
Important DSA topics include arrays, strings, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs, sorting, searching, recursion, and dynamic programming, as these are commonly asked in interviews and coding tests.
The best way to revise DSA is by revisiting key concepts, solving previously attempted problems, summarizing notes, and practicing regularly. Revision helps strengthen memory and improves problem-solving speed.
Explore Our Free Tech Tutorials









Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Comments (0)
No comments yet.