Front-end development focuses on building the visual and interactive parts of a website that users see and use every day. It includes designing layouts, styling pages, and adding interactivity using technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. A front-end developer ensures websites look good, load fast, and work smoothly across different devices and browsers, creating a great user experience.
This front-end developer roadmap provides a clear and structured learning path for beginners and aspiring developers. It explains what skills to learn, the correct order to follow, and how each technology fits into real-world development. By following this roadmap, you can avoid confusion, learn step by step, and confidently prepare for modern front-end developer roles.
Who is a Front-end Developer?
A front-end developer is a professional who creates the visual and interactive parts of a website or web application. They focus on how a site looks, feels, and responds to user actions by converting designs into responsive web pages using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Front-end developers work closely with designers and backend developers to ensure websites are attractive, easy to navigate, and perform smoothly across different devices and browsers. Their primary goal is to deliver a fast, user-friendly, and engaging experience for visitors.
Key Responsibilities of a Frontend Developer
- Design, build, and maintain responsive and interactive user interfaces using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
- Convert UI/UX designs, wireframes, and mockups into clean, functional, and visually accurate web pages
- Ensure cross-browser compatibility and smooth performance across desktops, tablets, and mobile devices
- Develop dynamic features, animations, and user interactions to improve engagement and usability
- Optimize front-end code for speed, performance, SEO, and scalability
- Integrate APIs and backend services while handling data rendering on the client side
- Debug, test, and fix UI issues to maintain stability and improve user experience
- Collaborate closely with designers, backend developers, and stakeholders to deliver complete solutions
- Follow accessibility standards, web best practices, and modern front-end development guidelines
Why Choose Front-end Development?
Front-end development is a popular career choice for those who enjoy creativity and technology. It allows you to build visually appealing and interactive websites while working with modern tools and frameworks used in real-world applications.
- Creative and Visual Work: Front-end development lets you turn ideas and designs into real interfaces, combining creativity with code to build attractive, interactive, and user-friendly web experiences.
- High Career Demand: Almost every business needs a modern website or web application, which creates continuous demand for skilled front-end developers across startups, enterprises, and global tech companies.
- Quick Learning with Instant Results: You can see changes instantly in the browser while coding, making learning faster, more engaging, and easier to understand for beginners.
- Career Growth and Flexibility: Front-end developers can grow into roles like UI engineer, full-stack developer, or technical lead, and enjoy flexible work options, including remote and freelance opportunities.
Choosing front-end development gives you the opportunity to create real-world products, improve your skills continuously, and design engaging user experiences that people interact with every day across the web.
Recommended Professional Certificates
Full Stack Development Mentorship Program
WordPress Bootcamp
Frontend Developer Roadmap 2026: Step-by-Step Learning Guide
This roadmap for front-end developers provides a clear, step-by-step learning path that helps beginners understand what to learn, the right order to follow, and how skills connect to real-world development.
Below are the steps that help you become a skilled front-end developer:
- Learn Computer Basics
- Understand the Internet and Web Basics
- Master HTML (Structure of Web Pages)
- Learn CSS Fundamentals
- Responsive and Mobile-First Design
- Understand JavaScript Fundamentals
- Learn Advanced JavaScript (ES6+)
- Version Control with Git and GitHub
- Learn Modern Front-end Frameworks and Libraries
- Advanced React Concepts
- Work with APIs and Backend Integration
- Package Managers and Build Tools
- Browser Developer Tools and Debugging
- Testing Basics for Front-end
- Web Performance Optimization
- Web Accessibility (a11y)
- SEO Basics for Front-end Developers
- Deployment and Hosting
- Build Real-World Projects
- Prepare for Front-end Developer Jobs
Now, we will go through each step one by one to clearly explain what you should learn, which key concepts to focus on, and how each step helps you grow as a confident front-end developer.
Step 1: Learn Computer Basics
Learning computer basics is the first step in becoming a front-end developer. It focuses on understanding how computers work and how to use them effectively. You should learn about operating systems, files and folders, basic hardware components, and simple commands. This foundation helps you navigate development tools, manage projects, install software, and work confidently before moving into web and front-end technologies.
Step 2: Understand the Internet and Web Basics
Before starting front-end development, it is important to understand how the internet and the web work. These basics explain how websites are accessed, how data travels across the internet, and how browsers display content. This knowledge helps you write cleaner code and understand real-world web behavior.
- How the Internet Works: The internet connects millions of devices worldwide, allowing them to share and exchange data through standard communication protocols.
- HTTP and HTTPS Protocols: HTTP and HTTPS define how information is requested, transferred, and delivered between a user’s browser and a web server.
- Domain Names: Domain names are human-readable web addresses that direct users to specific websites on the internet.
- Web Hosting: Web hosting stores website files on servers and makes them available to users through the internet.
- Domain Name System (DNS): DNS translates domain names into IP addresses so computers can locate and load websites correctly.
- Web Browsers: Web browsers are applications that load, display, and allow users to interact with web pages.
These concepts create a strong foundation for front-end development and help you work confidently with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript when building real-world web projects.
Step 3: Master HTML (Structure of Web Pages)
HTML is an essential part of web development and is used to structure web pages. It helps browsers understand, organize, and display content correctly through elements and tags. A strong understanding of HTML is necessary before moving on to styling or scripting.
- HTML Basics: Learn core concepts such as tags, elements, attributes, headings, paragraphs, links, images, lists, tables, and the basic structure of a web page.
- Semantic HTML: Use meaningful tags like header, section, article, and footer to improve page structure, accessibility, and search engine optimization.
- HTML Forms: Create forms to collect user input using input fields, labels, buttons, and built-in validation attributes.
- HTML5 Features: Understand modern features such as audio, video, canvas, local storage, and new semantic elements for building modern websites.
Mastering HTML gives you a strong foundation for CSS and JavaScript, allowing you to build well-structured, accessible, and modern web pages with confidence. Visit our HTML Tutorial to learn HTML in depth with simple and clear examples.
Step 4: Learn CSS Fundamentals
CSS is used to style and design web pages. It controls how HTML elements appear on the screen, including layout, colors, fonts, spacing, and responsiveness. Learning CSS helps transform simple HTML pages into visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces.
- CSS Basics: Learn selectors, properties, values, and how CSS connects with HTML using external, internal, and inline styles.
- Box Model: Understand margins, borders, padding, and content areas to control spacing and element sizing.
- Layout Techniques: Use Flexbox and Grid to build modern, flexible, and responsive layouts for different screen sizes.
- Colors and Typography: Work with color formats, fonts, text alignment, spacing, and readability to improve design quality.
- Responsive Design: Use media queries and relative units to ensure websites look good on mobiles, tablets, and desktops.
- Transitions and Animations: Add smooth hover effects and simple animations to improve user interaction.
Mastering CSS fundamentals helps you design clean, well-structured, and responsive interfaces that work smoothly across different devices and browsers, improving usability, accessibility, and overall user experience in modern web applications. Explore our CSS Tutorial to learn CSS in depth and enhance usability, accessibility, and overall user experience.
Upcoming Masterclass
Attend our live classes led by experienced and desiccated instructors of Wscube Tech.
Step 5: Responsive and Mobile-First Design
Responsive and mobile-first design ensures that websites look and work well on all screen sizes, including mobiles, tablets, and desktops. Since most users access websites on mobile devices, designing for smaller screens first helps create faster, cleaner, and more user-focused interfaces.
- Mobile-First Approach: Start designing layouts for small screens, then enhance them for larger devices.
- Responsive Layouts: Use flexible grids, percentages, and fluid layouts instead of fixed widths.
- Media Queries: Apply CSS rules based on screen size, resolution, and device type.
- Flexible Images: Ensure images and media scale properly without breaking layouts.
- Modern CSS Tools: Use Flexbox, Grid, and responsive units like rem, %, and vw to build adaptable layouts efficiently.
Learning responsive and mobile-first design helps you build user-friendly websites that perform well across devices and meet modern web standards.
Step 6: Understand JavaScript Fundamentals
JavaScript is a core programming language that adds interactivity and logic to web pages. It enables websites to respond to user actions, update content dynamically, and create interactive features that enhance the overall user experience.
- JavaScript Basics: Learn variables, data types, operators, and basic syntax used to write JavaScript programs.
- Control Structures: Understand conditions, loops, and decision-making to control program flow.
- Functions: Understand how functions help group logic and make code easier to reuse and manage.
- Arrays and Objects: Work with collections of data using arrays and objects.
- DOM Basics: Understand how JavaScript interacts with HTML and CSS through the Document Object Model.
Strong JavaScript fundamentals enable you to create dynamic and interactive websites, improve problem-solving skills, and prepare you to understand advanced JavaScript concepts and work confidently with modern front-end frameworks and libraries.
Step 7: Learn Advanced JavaScript (ES6+)
Advanced JavaScript introduces modern features that help you write cleaner, more efficient, and scalable code. These concepts are essential for building complex applications and working with modern front-end frameworks.
- ES6+ Features: Learn let and const, arrow functions, template literals, destructuring, spread operators, and modules.
- Asynchronous JavaScript: Understand callbacks, promises, async, and await to handle asynchronous operations smoothly.
- Advanced Functions: Work with closures, higher-order functions, scope, and hoisting.
- Error Handling: Learn to manage errors using try–catch blocks and proper debugging techniques.
- Working with APIs: Use modern methods like fetch to send and receive data from servers.
Advanced JavaScript skills help you write clean, maintainable code, handle complex logic, and work confidently with modern frameworks like React while building scalable front-end applications. Explore our JavaScript Tutorial to learn JavaScript in depth and work confidently with modern front-end frameworks and libraries.
Step 8: Version Control with Git and GitHub
Version control is an essential skill for every front-end developer. Git helps you track code changes, manage different versions of a project, and safely experiment without breaking existing work. GitHub is a cloud platform that stores Git repositories and allows developers to collaborate efficiently.
- Git Basics: Learn how Git tracks changes and manages versions using commands such as init, add, commit, and status.
- Working with GitHub: Understand how to create and manage repositories, clone projects, push and pull code, and keep local and remote code synchronized.
- Branching and Merging: Use branches to develop features separately and merge them safely into the main codebase.
- Collaboration Workflow: Work with teams using pull requests, code reviews, and issue tracking.
Mastering Git and GitHub enables you to manage projects efficiently, collaborate smoothly with teams, track code changes accurately, and follow industry-standard workflows essential for real-world front-end development and job-ready applications.

Step 9: Learn Modern Front-end Frameworks and Libraries
Modern front-end frameworks and libraries help you build fast, interactive, and scalable web applications. They simplify UI development, reduce repeated code, and improve application structure. Learning these tools is important for creating modern, production-ready front-end projects used in real-world development.
Libraries
- React: A popular JavaScript library used to build interactive, component-based user interfaces efficiently.
Frameworks
- Angular: A full-featured framework for building large, structured, and scalable web applications.
- Vue: A lightweight and flexible framework that is easy to learn and powerful for modern UI development.
Learning modern frameworks and libraries helps you develop professional front-end applications, handle complex UI logic, and work confidently in real-world development environments.
Step 10: Advanced React Concepts
Advanced React concepts help you build scalable, high-performance, and maintainable front-end applications. At this stage, you move beyond basics and learn how to manage complex state, improve performance, and structure large React projects effectively.
- Hooks in Depth: Understand useEffect, useContext, useReducer, useMemo, and useCallback for better state and logic management.
- State Management: Work with tools like Context API, Redux, or Zustand to handle global application state.
- Component Optimization: Learn memoization, lazy loading, and code splitting to improve performance.
- Routing: Use React Router to manage navigation and dynamic routes in single-page applications.
- Reusable Components: Build clean, reusable, and scalable component architectures.
Learning advanced React concepts helps you create production-ready applications, handle complex UI logic, and prepare for real-world front-end and MERN stack projects.
Step 11: Work with APIs and Backend Integration
Working with APIs and backend integration allows front-end applications to communicate with servers and display real data. This step focuses on connecting user interfaces with backend services, handling data flow, and managing asynchronous operations for real-world applications.
- Understanding APIs: Learn what APIs are and how REST APIs work to send and receive data between the frontend and backend.
- HTTP Methods: Use GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE methods to perform different operations on server data.
- Fetching Data: Work with tools like Fetch API and Axios to request and handle data from servers.
- Handling Async Operations: Manage asynchronous code using promises and async/await for smooth data loading.
- Authentication Basics: Understand tokens, headers, and basic authentication flows used in front-end applications.
- Error Handling: Handle API errors, loading states, and edge cases to improve user experience.
Learning API integration helps you build dynamic, data-driven applications and prepares you to work confidently with full-stack and MERN stack projects.
Explore More Career Roadmaps
Step 12: Package Managers and Build Tools
Package managers and build tools help you manage project dependencies and automate development tasks. They make front-end development faster, cleaner, and more efficient by handling libraries, bundling code, and optimizing assets for production use.
- Package Managers: Learn tools like npm and Yarn to install, update, and manage third-party libraries and dependencies used in front-end projects.
- Module Bundlers: Understand tools such as Vite, Webpack, or Parcel that bundle code, optimize assets, and prepare applications for deployment.
- Task Runners: Use build scripts to automate tasks such as compiling code, minifying files, and cleaning builds.
- Environment Configuration: Work with environment variables to manage development and production settings.
- Development Servers: Use local servers with hot reload for faster development and testing.
Understanding package managers and build tools helps you maintain organized projects, improve performance, and work efficiently in real-world front-end development workflows.
Step 13: Browser Developer Tools and Debugging
Browser developer tools help you inspect, test, and debug front-end code directly in the browser. They allow you to identify issues quickly, understand how your code runs, and improve website performance and behavior during development.
- HTML & CSS Inspection: Use the Elements panel to inspect, edit, and debug HTML and CSS in real time.
- JavaScript Debugging: Use breakpoints, console logs, and error tracking to efficiently fix JavaScript issues.
- Network Monitoring: Analyze requests, responses, APIs, and loading times to find performance problems.
- Performance Analysis: Measure rendering speed, memory usage, and runtime performance.
- Responsive Testing: Test layouts across different screen sizes and devices.
Strong debugging skills help you write cleaner code, fix problems faster, and build reliable front-end applications.
Step 14: Testing Basics for Front-end
Testing ensures that front-end applications work correctly and remain stable as they grow. It helps you catch bugs early, improve code quality, and maintain a smooth user experience across updates and features.
- Why Testing Matters: Understand how testing reduces errors and improves long-term reliability.
- Unit Testing: Test individual components and functions using tools like Jest.
- Component Testing: Verify UI behavior and rendering with React Testing Library.
- End-to-End Testing: Simulate real user interactions using tools like Cypress or Playwright.
- Debugging Test Failures: Learn to read test reports and fix failing tests efficiently.
Basic testing skills help you build stable, confident, and production-ready front-end applications.
Step 15: Web Performance Optimization
Web performance optimization focuses on making websites load faster and run smoothly. Better performance improves user experience, reduces bounce rates, and helps applications perform well across devices and network conditions.
- Optimizing Assets: Compress images, minify CSS and JavaScript, and reduce unused code.
- Efficient Loading: Use lazy loading, code splitting, and caching to improve load times.
- Rendering Optimization: Reduce reflows and repaints for smoother UI interactions.
- Network Optimization: Improve API calls and use CDN services to speed up content delivery.
- Performance Monitoring: Measure and analyze performance using browser tools and audits.
Performance optimization helps you deliver fast, reliable, and high-quality front-end applications.
Step 16: Web Accessibility (a11y)
Web accessibility ensures that websites can be used by everyone, including people with disabilities. Accessible design improves usability, reaches a wider audience, and follows modern web standards and best practices.
- Semantic HTML: Use proper elements to improve screen reader support and structure.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure all features work using only a keyboard.
- ARIA Attributes: Apply ARIA roles and labels to enhance accessibility where needed.
- Color and Contrast: Maintain readable text with proper color contrast.
- Accessible Forms: Use clear labels, error messages, and focus states.
Accessibility knowledge helps you create inclusive, easy-to-use front-end applications that follow web standards and provide better experiences for all users.
More Blog Topics to Read
| Web Design Vs Web Development | Java vs JavaScript |
| Magento Vs WooCommerce | HTML Vs HTML5 |
| Frontend Vs Backend Development | Coding Vs Programming |
Step 17: SEO Basics for Frontend Developers
SEO basics help front-end developers make websites easier to discover through search engines. Proper SEO improves visibility, increases traffic, and ensures content is indexed and displayed correctly.
- Semantic HTML: Use meaningful tags to help search engines understand page structure.
- Meta Tags: Optimize titles, descriptions, and viewport settings.
- Page Speed: Improve loading performance to support better rankings.
- Mobile Optimization: Ensure pages work well on all devices.
- Clean URLs: Create readable and search-friendly URLs.
SEO knowledge helps you build search-friendly, user-focused front-end applications. You can also explore the SEO roadmap to gain a deeper understanding and improve website visibility effectively.
Step 18: Deployment and Hosting
Deployment and hosting involve making your front-end application available on the internet. This step helps you understand how projects move from local development to live environments that users can access.
- Hosting Platforms: Learn platforms like Netlify, Vercel, and GitHub Pages for front-end hosting.
- Build Process: Understand how production builds are created and deployed.
- Environment Settings: Manage environment variables for different setups.
- Domain Setup: Connect custom domains and configure basic DNS settings.
- Continuous Deployment: Automatically deploy updates from Git repositories.
Deployment skills help you confidently publish, manage, and maintain live front-end applications.
Step 19: Build Real-World Projects
Building real-world projects helps you apply front-end concepts in practical scenarios and understand how real applications are built. Projects improve problem-solving skills, strengthen technical knowledge, and help you create a strong portfolio that showcases your abilities.
To explore practical ideas, you can check our 20 Front-end Development Projects Ideas here, which features beginner to advanced project ideas designed to sharpen skills and prepare you for real-world front-end development roles.
Step 20: Prepare for Front-end Developer Jobs
Preparing for front-end developer jobs involves refining your technical skills and understanding industry expectations. Focus on strengthening HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and modern frameworks while practicing problem-solving and real-world scenarios.
Build a strong portfolio that showcases your best projects, clean code, and responsive designs. Practice common interview questions, coding challenges, and system basics to improve confidence and communication during interviews.
You can explore our online full-stack course to learn front-end and back-end development together in a structured way. This program offers step-by-step guidance, real-world projects, expert mentorship, and job-ready skills that help you confidently start your front-end development career.
Career Path After Completing Front-end Development
After completing front-end development, many career options open up. Following a clear front-end development roadmap helps you choose the right role, grow skills, and move confidently into modern web development careers.
- Front-end Developer: Work on building responsive, interactive user interfaces using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and modern frameworks while focusing on performance, accessibility, and user experience.
- UI Engineer / UI Developer: Focus on translating designs into clean, reusable components, working closely with designers to deliver visually polished and user-friendly interfaces.
- Full Stack Developer: Expand front-end skills by learning backend technologies, APIs, and databases to build complete end-to-end web applications.
- JavaScript Developer: Specialize in JavaScript and related frameworks to build dynamic, scalable, and high-performance web applications.
With continuous learning and hands-on projects, front-end development offers long-term growth, flexibility, and opportunities across startups, enterprises, and global tech companies.
Front-end Developer Demand and Salary in India (2026)
With businesses rapidly moving online, the need for modern websites and web applications is increasing across industries. The global web development market is projected to grow significantly and reach $8 trillion by 2027, highlighting strong long-term demand for front-end developers in India and worldwide.
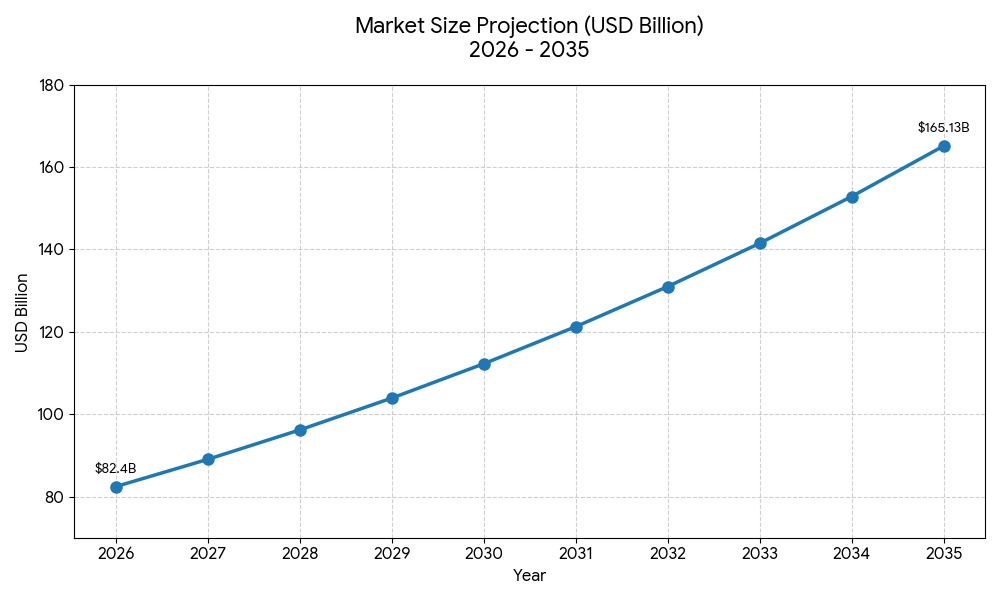
In India, companies are actively hiring front-end developers who can build responsive, user-friendly, and high-performance interfaces. Skills in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and modern frameworks significantly improve job opportunities and salary growth.
Front-end Developer Salary in India
| Experience Level | Average Salary Range |
| Fresher (0–2 years) | ₹3 LPA – ₹6 LPA |
| Mid-Level (2–5 years) | ₹6 LPA – ₹10 LPA |
| Experienced (5+ years) | ₹8 LPA – ₹15+ LPA |
With rising digital adoption, strong salary growth, and opportunities across startups, enterprises, and global companies, front-end development remains a stable and rewarding career choice in India for 2026 and beyond.
Front-end Developer Roadmap (Detailed Video Guide)
FAQs About Front-end Developer Roadmap
Front-end development is about creating the parts of a website that users interact with on their screens. You use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to design page structure, styling, and interactive behavior that works smoothly inside web browsers.
Yes, a front-end developer roadmap for beginners is ideal if you are starting from scratch. You learn basics first, like HTML and CSS, then gradually move to JavaScript, frameworks, projects, and job preparation without feeling overwhelmed.
If you practice regularly, you can follow a front-end developer learning roadmap in about six to twelve months. Your progress depends on consistency, project practice, and how deeply you understand concepts instead of rushing through topics.
No prior coding experience is required to start front-end development. You begin with simple concepts like HTML structure and basic styling, then slowly build coding skills through practice, examples, and real projects as you move forward.
The most important skills include HTML, CSS, JavaScript, responsive design, Git, and modern frameworks like React. Along with technical skills, you also need problem-solving, debugging, and basic design understanding to build real applications.
React is not mandatory, but it is highly recommended in a front-end developer’s full roadmap. Many companies use React, and learning it helps you build modern applications, manage UI efficiently, and improve your job opportunities significantly.
No, you do not need a formal degree. If you follow a proper frontend roadmap, practice regularly, and build real projects, you can get job-ready based on skills rather than qualifications.
You should build projects like landing pages, portfolios, dashboards, forms, and small applications. Projects help you apply concepts, improve confidence, and showcase your skills to employers while following a roadmap of front-end developer learning.
Front-end development is a strong career choice in 2026 because businesses need modern websites and applications. If you follow a clear front-end developer roadmap and keep learning, you can access high-demand roles and long-term growth.
Free Courses for You




![Full Stack Course Fee and Duration [Details]](https://www.wscubetech.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/full-stack-course-details-300x145.webp)


Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Comments (0)
No comments yet.