Backend development focuses on the server-side part of applications that users do not directly see. It involves working with servers, databases, APIs, and application logic to process data securely and efficiently. Backend systems ensure applications run smoothly, handle user requests correctly, and remain scalable as traffic grows. Strong backend development is essential for building reliable, high-performance web and mobile applications used in real-world environments.
This backend developer roadmap provides a clear and structured learning path for mastering backend skills. It guides learners on what to learn first and how to progress step by step without confusion. By following this roadmap, beginners can build strong fundamentals, avoid random learning, and develop practical, job-ready backend skills with confidence.
Who is a Backend Developer?
A backend developer is a professional who builds and manages the server-side part of applications. They focus on how websites and apps work behind the scenes, including servers, databases, and application logic that users do not see directly.
Backend developers ensure data is processed correctly, securely, and efficiently. They work closely with frontend developers to connect user interfaces with backend systems and help deliver fast, reliable, and scalable applications.
Key Responsibilities of a Backend Developer
- Design, develop, and maintain robust server-side logic to ensure applications run smoothly, handle requests efficiently, and deliver consistent performance.
- Manage databases by storing, retrieving, and organizing data securely while maintaining accuracy, efficiency, and optimal performance.
- Create, integrate, and maintain APIs that enable seamless communication between frontend interfaces and backend systems.
- Implement security measures, improve scalability, and optimize performance to support growing users and high traffic loads.
- Debug, test, and maintain backend code regularly to identify issues, improve stability, and ensure reliable application behavior.
Also Read: Top 20 Front-end Development Projects
Why Follow a Backend Developer Roadmap?
Following a backend developer roadmap helps you learn backend development in a clear and structured way. It shows you what to learn, in what order, and how skills connect, saving time and helping you build strong, job-ready backend development knowledge.
- Clear Learning Path: A roadmap removes confusion by showing the right sequence of topics, from basic programming to advanced backend concepts.
- Focus on Essential Skills: It helps you concentrate on in-demand backend technologies, tools, and practices required by real-world applications.
- Better Career Preparation: Learning through a roadmap improves confidence, practical understanding, and readiness for backend developer roles.
If you want a guided path instead of figuring everything out on your own, you can join our Full Stack Web Development Online Course, where we cover frontend, backend, databases, and deployment step by step with live mentorship.
Recommended Professional Certificates
Full Stack Development Mentorship Program
WordPress Bootcamp
Backend Developer Roadmap: Step-by-Step
Below, we have shared a step-by-step guide to help you learn and become job-ready.
- Internet Basics and How the Web Works
- Learn Programming Fundamentals
- Learn Backend Frameworks and Server-Side Development
- Work with Databases (SQL and NoSQL)
- Understand APIs and Web Services
- Learn Authentication, Authorization, and Security Basics
- Handle Caching, Sessions, and Performance Optimization
- Learn Version Control and Collaboration Tools
- Understand DevOps Basics and Deployment
- Work with Cloud Platforms and Backend Infrastructure
- Build Real-World Backend Projects and Portfolio
- Prepare for Backend Developer Jobs and Interviews
Now, each step will be explained in detail, covering what to learn, why it matters, and how it helps you grow from a beginner to a confident, job-ready backend developer with practical, real-world skills.
Step 1: Understand Internet Basics and How the Web Works
Internet basics explain how data moves between users and servers across the web. When you open a website, your browser sends a request to a server using protocols like HTTP or HTTPS. The server processes the request and sends back a response, which the browser displays. Concepts like IP addresses, domain names, DNS, and hosting help connect users to the correct servers. Understanding how the web works is important for backend developers because it explains request–response flow, client–server architecture, and how applications communicate over the internet.
Step 2: Learn Programming Languages
Learning a programming language is a key step in backend development. Backend languages are used to build server-side logic, handle requests, manage databases, and run application workflows. A strong understanding of one backend language helps you write clean code, learn frameworks easily, and build scalable backend systems. The right language choice depends on project needs, career goals, and industry demand.
Popular Backend Programming Languages
- Python: Easy to learn and commonly used for backend development, APIs, and data-driven applications. It has powerful frameworks like Django and Flask and a large developer community.
- Java: Commonly used in enterprise-level applications. Java is known for strong performance, scalability, and frameworks like Spring Boot used in large backend systems.
- JavaScript (Node.js): Allows backend development using JavaScript. Node.js is popular for building fast, scalable, and real-time applications with a single language across frontend and backend.
- PHP: Widely used for web development and content-driven websites. PHP works well with databases and powers many popular platforms and backend systems.
- Go (Golang): Known for simplicity and high performance. Go is often used for building scalable, cloud-based, and microservices-driven backend applications.
These languages help you build strong backend foundations, work with frameworks, connect databases, and develop efficient, real-world backend applications.
Step 3: Learn Backend Frameworks and Server-Side Development
Backend frameworks make server-side development faster, cleaner, and more organized. They provide built-in features for handling requests, routing, security, and database integration, allowing you to focus more on application logic instead of setup. Server-side development involves creating backend code that processes requests, applies rules, works with databases, and returns responses. Learning frameworks helps you understand how real-world backend applications are structured and scaled.
Frameworks are important to accelerate development:
- Express.js (Node.js)
- Django / Flask (Python)
- Spring Boot (Java)
- Laravel (PHP)
Learning these frameworks helps you build production-ready backend applications faster, follow best practices, and prepare for real-world backend development used in modern companies.
Step 4: Work with Databases (SQL and NoSQL)
Databases are a core part of backend development because they store and manage application data. Backend developers rely on databases to save user information, application records, and system data securely. Learning how to design database schemas, write efficient queries, and manage data helps ensure applications remain fast, consistent, and scalable. Understanding both SQL and NoSQL databases prepares you to handle different backend use cases.
- SQL Databases: Use structured tables with fixed schemas and clear relationships. They are ideal for applications that require structured data, strong consistency, and complex queries. Common examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
- NoSQL Databases: Store data in flexible formats such as documents, key-value pairs, or collections. They work well for large-scale, high-traffic, and rapidly changing data applications. Popular examples include MongoDB, Redis, and Cassandra.
SQL vs NoSQL: Choosing the Right Database
Choose SQL databases when your application needs structured data, clear relationships, and strong consistency. Choose NoSQL databases when your application requires flexibility, high scalability, and fast performance for large or frequently changing data.
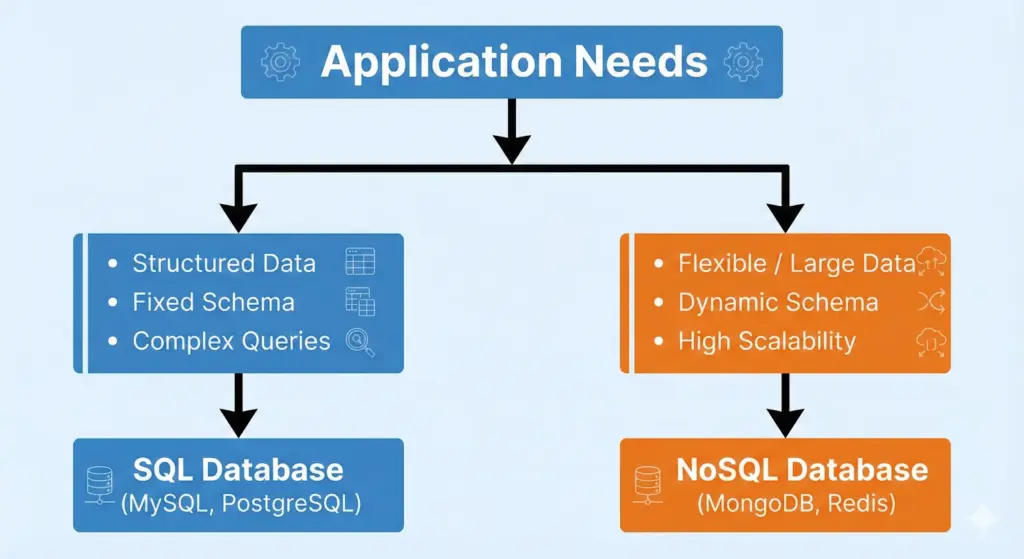
Understanding when to use SQL or NoSQL helps you design efficient backend systems, choose the right storage solution, and build scalable applications suited for real-world production environments.
Step 5: Understand APIs and Web Services
APIs, or Application Programming Interfaces, enable communication between different software systems. In backend development, APIs act as a bridge between servers, frontend applications, mobile apps, and external services. They define how data is requested, processed, and delivered in a structured and secure format, allowing different systems to work together smoothly.
Backend developers use APIs to expose application features, fetch or update data, and integrate third-party services such as payment gateways or messaging tools. Well-designed APIs improve scalability, maintainability, and security in real-world applications.
Key API Concepts
- REST (Representational State Transfer): A widely used approach for building web services that relies on standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. REST APIs are simple, scalable, and easy to maintain.
- GraphQL: A modern API query language that allows clients to request only the specific data they need. This reduces over-fetching, improves performance, and gives more flexibility to frontend applications.
Learning how to design, build, and consume APIs is a core backend skill, as APIs power most modern web and mobile applications and enable seamless communication between systems.
Explore More Career Roadmaps
Step 6: Learn Authentication, Authorization, and Security Basics
Security is an important part of backend development. Backend developers must safeguard applications from unauthorized access, data leaks, and common security risks. Authentication and authorization help ensure that only verified users can access the application and that their actions are limited based on assigned permissions. Understanding security fundamentals helps you build safe, trustworthy, and production-ready backend systems.
- Authentication: Verifies a user’s identity using login credentials, tokens, or trusted third-party authentication providers before granting access.
- Authorization: Defines the actions and resources an authenticated user is permitted to use within an application.
- Password Security: Learn password hashing, salting, and secure storage practices to protect user credentials.
- Session Management: Understand how sessions, cookies, and tokens manage user state securely.
- JWT and Tokens: Use JSON Web Tokens for secure and stateless authentication in modern applications.
- Common Security Threats: Learn about SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
- HTTPS and Encryption: Secure data in transit using HTTPS and basic encryption techniques.
Learning authentication, authorization, and security basics helps you build backend systems that are secure, reliable, and ready for real-world usage.
Step 7: Handle Caching, Sessions, and Performance Optimization
Performance plays a major role in backend development. Backend developers must ensure that applications load quickly, respond smoothly, and handle high user traffic without crashing. Techniques like caching, session management, and performance optimization help reduce server load, improve response times, and provide a better overall user experience.
As applications scale, inefficient backend logic or database usage can slow systems down. Learning performance fundamentals helps you design backend systems that remain fast, stable, and reliable in production environments.
- Caching: Keeps commonly accessed data ready for quick access, reducing database workload and improving application response time.
- Sessions: Manage user state across multiple requests using sessions, cookies, or tokens.
- Load Handling: Handle multiple user requests efficiently without slowing down the system.
- Query Optimization: Improve database queries to reduce processing time and resource usage.
- Scalability Basics: Design backend systems that can grow smoothly as traffic increases by distributing load and using efficient system architecture.
Learning these areas helps you build fast, efficient, and scalable backend applications for real-world use.
Upcoming Masterclass
Attend our live classes led by experienced and desiccated instructors of Wscube Tech.
Step 8: Learn Version Control and Collaboration Tools
Version control is an essential skill for backend developers. It helps you track code changes, manage different versions of a project, and work safely without losing progress. Version control systems allow developers to revert mistakes, experiment with new features, and maintain a clear history of code updates.
In real-world projects, backend development is usually done in teams. Collaboration tools make it easy for multiple developers to work on the same codebase, review changes, resolve conflicts, and maintain code quality. Learning these tools prepares you for professional development environments.
Common Version Control Systems include:
- Git: The most widely used version control system. It tracks changes, supports branching and merging, and works well for both small and large projects.
- GitHub: A popular Git-based platform used for hosting repositories, managing pull requests, and collaborating with teams.
- GitLab: Provides repository hosting along with built-in CI/CD tools for automated testing and deployment.
- Bitbucket: A Git-based platform often used in enterprise environments and integrated with project management tools.
Benefits of Version Control
- Keeps a complete history of code changes
- Helps multiple developers work on the same project without conflicts
- Makes it easy to fix bugs by rolling back to earlier versions
- Supports branching for safe feature development and testing
- Improves collaboration, code quality, and project organization
Mastering version control and collaboration tools helps you work confidently in teams, follow industry standards, and contribute effectively to real-world backend projects.
Step 9: Understand DevOps Basics and Deployment
DevOps focuses on combining development and operations to deliver applications faster and more consistently. For backend developers, understanding DevOps basics helps in deploying applications, managing servers, and ensuring systems run smoothly in production. It reduces manual work and improves collaboration between development and operations teams.
Deployment is the process of moving backend applications from development to live environments. Learning how deployment works helps you release updates, fix bugs, and scale applications with confidence. Important DevOps concepts to learn:
- CI/CD Pipelines: Automate code testing, building, and deployment processes to enable faster, safer, and more consistent application releases.
- Containers (Docker): Package backend applications along with all dependencies so they run consistently across different environments, from local machines to production servers.
- Cloud Platforms: Use services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud to host and scale backend applications.
- Monitoring and Logging: Track application performance, monitor system health, and detect errors or failures in real time within production environments.
- Infrastructure Basics: Understand servers, environments (development, staging, production), networking basics, and configuration management.
DevOps and deployment knowledge helps backend developers release applications smoothly, manage production systems efficiently, and ensure applications remain stable, scalable, and well-maintained in real-world environments.
Step 9: Work with Cloud Platforms and Backend Infrastructure
Cloud platforms provide the tools and services needed to run backend applications at scale. They help you deploy servers, manage databases, handle storage, and control networking without managing physical hardware. Understanding cloud infrastructure allows backend developers to build scalable, cost-effective, and highly available applications. Learning how backend systems run in the cloud is essential for modern, production-ready development.

Step 10: Build Real-World Backend Projects and Portfolio
Building real-world backend projects helps you apply backend concepts in practical situations. Projects give hands-on experience with APIs, databases, authentication, and server-side logic. They also help you understand how backend systems manage data, handle user requests, and support application performance in real environments.
Working on multiple projects improves problem-solving skills and technical confidence. You learn how to structure backend code, integrate databases, handle errors, and secure applications. These experiences prepare you to work on real production-level systems and understand how backend components work together.
A strong backend portfolio increases your chances of getting hired. It shows employers that you can build complete backend solutions, not just study theory. You can also check backend project ideas to practice different scenarios and create projects that demonstrate real-world backend development skills.
Step 11: Prepare for Backend Developer Jobs and Interviews
Preparing for backend developer roles involves strengthening core backend concepts such as programming languages, databases, APIs, authentication, and system design. Regular practice with coding problems, backend scenarios, and real-world use cases helps improve logic and confidence. Reviewing common backend interview questions also helps you explain concepts clearly and accurately.
Interview preparation should also focus on projects and practical experience. Be ready to discuss backend projects, design decisions, challenges faced, and how problems were solved. Understanding basic system design, performance optimization, and security concepts helps you perform better in technical and practical interview rounds.
Career Opportunities After Learning Backend Development
Completing a structured backend developer roadmap opens doors to high-demand roles where backend skills power scalable applications and reliable systems. Below are career opportunities you can explore after building strong backend development skills.
- Backend Developer: Responsible for server-side logic, database management, API development, and application performance. This role focuses on building stable, secure, and scalable systems that power websites and mobile applications behind the scenes.
- API Developer: Specializes in designing, building, and maintaining RESTful or GraphQL APIs that connect frontend interfaces, mobile apps, and third-party services, ensuring smooth data exchange and consistent application functionality.
- Cloud Engineer: Works with cloud platforms to deploy, manage, and scale backend infrastructure. This role ensures system availability, performance optimization, and secure cloud-based backend environments for applications.
- DevOps Engineer: Combines backend knowledge with automation, deployment, and monitoring practices. DevOps engineers manage CI/CD pipelines, system reliability, and collaboration between development and operations teams.
Explore More Blog Topics
| Web Design Vs Web Development | Java vs JavaScript |
| Magento Vs WooCommerce | HTML Vs HTML5 |
| Frontend Vs Backend Development | Coding Vs Programming |
Backend Developer Salary in India (Freshers to Experienced)
Backend developers in India earn strong salaries because of their important role in building and maintaining applications. Industry salary insights indicate that the typical annual base pay for backend developers in India is close to ₹7.25 lakh, reflecting steady demand for this skill set.
Typical salary ranges in India include:
- Entry-level: ₹2–4 LPA
- Mid-level: ₹7–20 LPA
- Senior-level: ₹15–35+ LPA
Salaries vary depending on skills, experience, company type, and location. Startups may offer equity and bonuses, while established tech companies provide higher fixed packages.
Best Books for Backend Developer
Here are some of the best books every backend developer should consider to build strong technical foundations, improve coding quality, and understand real-world system design. These books are widely recommended by industry professionals and are suitable for both beginners and experienced developers.
1. “Designing Data-Intensive Applications” by Martin Kleppmann:

A deep dive into data systems, scalability, reliability, and performance, essential for understanding backend architecture.
2. “Clean Code” by Robert C. Martin:

Teaches practical principles for writing readable, maintainable, and high-quality code used in professional backend projects.
3. “The Pragmatic Programmer” by Andrew Hunt & David Thomas:

Offers timeless software development practices, problem-solving skills, and professional habits useful for backend engineers.
Backend Web Developer Roadmap (Video Guide)
FAQs About Backend Developer Roadmap
JavaScript with NodeJS is often recommended for beginners due to its high demand in today’s market, because it is part of the MERN Stack. However, the best language to start with can depend on your interests and the specific areas of backend development you want to pursue.
While a degree in computer science or a related field can be beneficial, it is not strictly necessary to become a backend developer. Many developers are self-taught or have transitioned from other fields, using online resources or website development course, bootcamps, and practical experience to build their skills.
The time required to become a backend developer depends on your background and learning pace. With consistent practice, beginners can gain job-ready backend skills in 6–12 months by learning programming, databases, APIs, and building real-world projects.
Anyone who wants to work on the server side of websites and applications can follow this roadmap. It is useful for beginners, students, career switchers, and even frontend developers who want to learn backend skills.
Backend development can feel more complex because it involves servers, databases, and logic. However, with the right roadmap and practice, it becomes easy to understand.
Yes, backend developers can work remotely. Many companies offer remote positions for developers, especially in today's digital-first world. The nature of backend development work, which primarily requires a computer and internet connection, makes it well-suited for remote work.
As a backend developer, you should learn at least one backend programming language such as Python, Java, JavaScript (Node.js), PHP, or Go. Understanding backend frameworks like Django, Spring Boot, Express.js, or Laravel is also important. You should work with databases (SQL and NoSQL), learn API development (REST and GraphQL), use version control tools like Git, and understand basics of cloud platforms, security, and deployment tools.
Yes, understanding frontend basics is helpful for backend developers. It improves API design, debugging, and teamwork with frontend developers. Basic knowledge of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript makes you more versatile and better prepared for real-world full-stack collaboration.
Building personal projects is one of the best ways to gain practical experience. Contributing to open-source projects, participating in coding challenges, and internships can also provide hands-on experience and strengthen your understanding of backend technologies.
Certifications can demonstrate your knowledge and commitment to professional development but are not always necessary. Practical experience, a strong portfolio, and a deep understanding of backend technologies are typically more important to employers.
Follow tech blogs, join developer communities, participate in forums, and attend webinars or conferences. Continuous learning and networking with other professionals are key to staying updated with the latest trends and technologies in backend development.
A backend developer specializes in server-side development, focusing on databases, server logic, and application architecture. A full-stack developer, on the other hand, has the skills to work on both the frontend and backend parts of web applications, handling everything from user interface design to server and database management.
Free Courses for You





![Full Stack Course Fee and Duration [Details]](https://www.wscubetech.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/full-stack-course-details-300x145.webp)
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Comments (0)
No comments yet.