When you search for something on Google, you get thousands of results. Google ranks different web pages on search engine result pages (SERPs), and you mostly prefer clicking on the top-ranked links.
Do you know why some website appear on the top of SERPs? It’s because of on-page SEO, which has the power to boost your search engine rankings and attract countless users to your website. It is one of the most critical components to improve online visibility.
Marketers and website owners take care of every on-page element. From deciding on the topics and creating content to enhancing user experience and more, they tweak each aspect according to the target audience. They choose relevant keywords to focus on to enhance a website’s ranking.
Let’s dive deeper into what on-page SEO means, its techniques, and elements critical to improving a website’s search engine ranking.

What Is On-Page SEO Optimization?
On-page SEO, also known as on-site SEO, refers to the process of optimizing web pages and content on the website to improve its search engine rankings. It includes tweaking links, content, tags, and web pages so that the website ranks higher on SERPs for queries related to the target keywords.
It improves a brand’s online search visibility and drives more organic traffic. In short, on-page SEO optimizes a website so that search engines can understand and trust it more, allowing it to rank higher on SERPs. Common on-page SEO elements include title tags, URLs, internal links, and blogs.
Upskill Yourself With Live Training (Book Free Class)
Why Is On-Page SEO Important?
Now that you are familiar with the definition of on-page SEO let’s understand why on-page SEO is important. On-page elements, such as blogs, URLs, meta tags, keywords, titles, etc., tell search engines all about your website. Google and other search engines use these on-page components to know if the website aligns with the user’s search intent and whether it provides value to visitors and customers. If it does, search engines serve it to users to answer specific queries.
Having an attractive website is not enough. You need to work on various on-page elements to keep up with the ever-changing Google algorithm. As search engines prioritize user experience and ‘people-first content’ while ranking web pages, you must optimize your website consistently to rank higher and attract organic traffic.
Moreover, you must create valuable and helpful content to match user intent and build authenticity. Hence, we use on-page SEO that optimizes a website for users and search engines, showing its relevance and usefulness for search engine rankings.
On-page SEO optimization includes changes and updates we make to different website elements that are visible to visitors. Website owners have complete control over every aspect of on-page SEO. Therefore, they must do it right.
Here are a few key reasons why on-page SEO is important:
- When we include relevant keywords in titles, headers, meta tags, and descriptions, it ensures that our content matches the search queries so target audience visits the website.
- On-page SEO increases the chances of ranking higher on SERPs and makes the website more visible.
- Google and other search engines prioritize mobile-friendly websites while ranking pages. On-page optimization makes a website compatible with mobile devices, which enhances user experience and influences its ranking.
- Optimizing and structuring a website allows users to navigate it easily.
- Optimized on-page elements give your business a competitive edge and make it a reliable brand in your niche.
Also Read: What is SEO in Digital Marketing? Beginners Guide
On-Page SEO Techniques
Below, we have discussed the top on-page optimization techniques that marketers must use to achieve the desired business and marketing goals. Let’s see how to do on-page SEO for better results:
- Optimize Title Tags
- Create a Keyword-rich URL
- Write an Attractive Meta Description
- Develop SEO-friendly Content
- Use Header Tags
- Build External Links
- Add Internal Links
- Optimize Images Using Alt Tags
1. Optimize Page Title
A page title or content title is a part of HTML code that shows what the main heading of your page is. This title is displayed in browser tabs, search engines, and social media posts. The title plays a crucial role in deciding if a user will click on your page or not. Your title looks like this on SERPs.
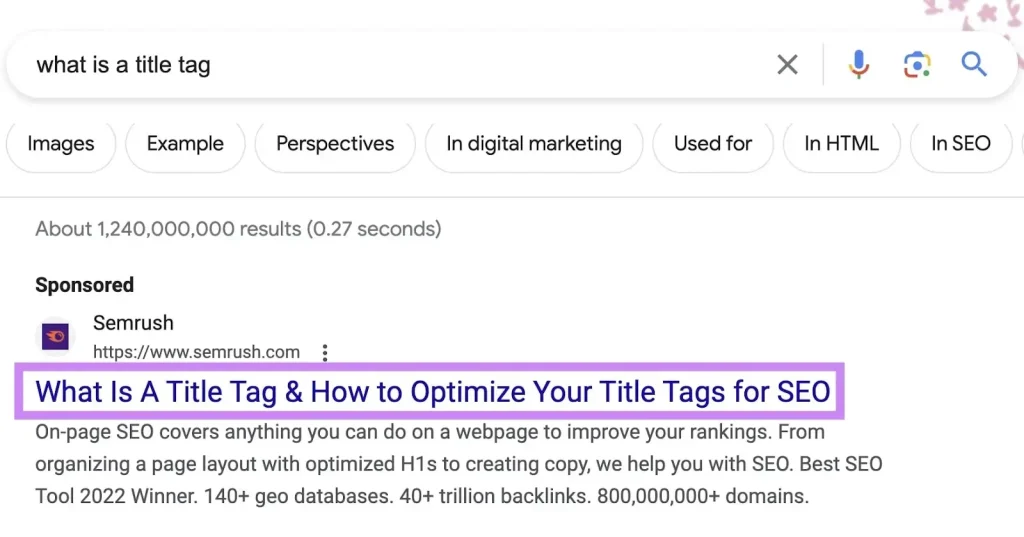
Here are a few factors you need to consider while generating title tags for your content or web page:
Keep it Brief: Your title should have between 50 to 60 characters so that Google doesn’t cut it off while displaying it in search results.
Use Keywords: Your title must include relevant keywords so that users and Google can know what your page is about. Don’t stuff keywords and use them naturally in the title.
Be Descriptive: Create a descriptive title that describes the content or goal of the page accurately.
Be Unique: Rather than copying another title, craft a unique title for each page to show its clear purpose to Google.
Avoid capitalizing every letter in the title.
If possible, include your brand name in the title.
2. Create a Keyword-rich URL
One of the primary on-page SEO factors is URL, which must be simple and brief. Google recommends using page address that is relevant to the content, as it enables users to determine what it is about. Don’t make it look intimidating or cryptic by generating a complex address.
Moreover, URLs shouldn’t contain full sentences, random numbers, or publish dates. Don’t use automatically generated URLs, as they can contain these elements by default. Make sure to edit the URL before publishing it. Also, use the target keywords so that the URL aligns with the topic of the content, which will enhance your SEO effort.
Here is an example of an unfriendly and inefficient URL:

An optimized and useful URL looks somewhat like this:

The more Google can understand the gist and context of your web page, the better it is for your search engine ranking. The search engine will be able to match that page with relevant search queries.
Here are a few tips to remember while generating a URL:
- Use just one or two keywords
- Avoid using unnecessary words
- Use HTTPs if possible because it’s one of the Google’s ranking factors
Also Read: How to Learn SEO in 2025? Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
3. Write an Attractive Meta Description
A meta description is an HTML element on a website. It is like a brief summary of the page describing to users and search engines what they can expect to find. A compelling and accurate description summarizing the content of the page can encourage users to click on the link.
You can see meta description below the page title on SERPs and it has the power to influence the actions of users. However, meta description doesn’t play much role in search engine ranking. Having said that, a unique and attractive description can make users visit your page, which can boost web traffic. Please remember that if your meta decsription doesn;t match the user’s intent, Google will generate its own description for SERPs.
Here are a few best practices to follow to craft a click-worthy description:
- Keep it between 150-160 characters so that the entire description is displayed in search results.
- For mobile devices, a meta description should have 120 characters.
- Add target keywords in the description to help search engines and users determine what your page is about. Google bolds relevant keywords that align with user intent and search query. As these keywords stand out, they increase the number of clicks.
- Use complete and interesting sentences. Also, use active voice as it saves space and conveys clearer messages.
- Avoid using alphanumeric characters.
- Try using CTA (call to action) phrases, such as find out more and try for free now, to get the attention of users.
4. Develop SEO-friendly Content
One of the most crucial on-page SEO steps is creating quality and optimized content that matches user intent. Along with adding keywords to your URL, title, and header, you must include target keywords throughout the content. However, they must fit naturally. Conduct keyword research to find relevant phrases and search terms to target and create a list of the most suitable keywords. Sort them by search volume and competition level to make an effective content strategy.
While filtering keywords, consider keyword difficulty as well. Short-tail keywords are difficult to rank and are more competitive. Startups and small businesses must opt for less competitive and long-tail keywords in the beginning. Once they mark the presence in the market, then they should move on to the more difficult ones.
You can use keyword research tools to find relevant keywords and analyze your competitors to get better content idea. Sort all the keywords into relevant categories, narrow down the list, and create topics based on different keywords.
While it’s important to use keywords for SEO, avoid keyword stuffing, which is excessive and repeated use of keywords in content to manipulate search engine rankings. Keyword stuffing can significantly impact the readability and user experience. It can also seem to be spammy and confuse readers. With modern search engines becoming smarter and more advanced, they monitor content meticulously to find keywords used unnaturally in content.
Here are the best practices for creating SEO-friendly and optimized content:
- Content must match users’ search intent and search terms they use to search for queries.
- Use keywords naturally in content and avoid keyword stuffing.
- Add visual content
- Answer a specific query to make it useful for users
- Create unique and engaging content to stay ahead of competitors.

5. Use Header Tags
Headings help users skim your content easily to find useful information and enable Google to understand the structure of your page and find if it aligns with user’s search intent. The search engine can understand the hierarchy of the page or content, so it can be displayed for relevant search queries.
The following image shows two different pieces of content. The one with no heading hardly compels users, but the one with proper heading tags looks more organized.
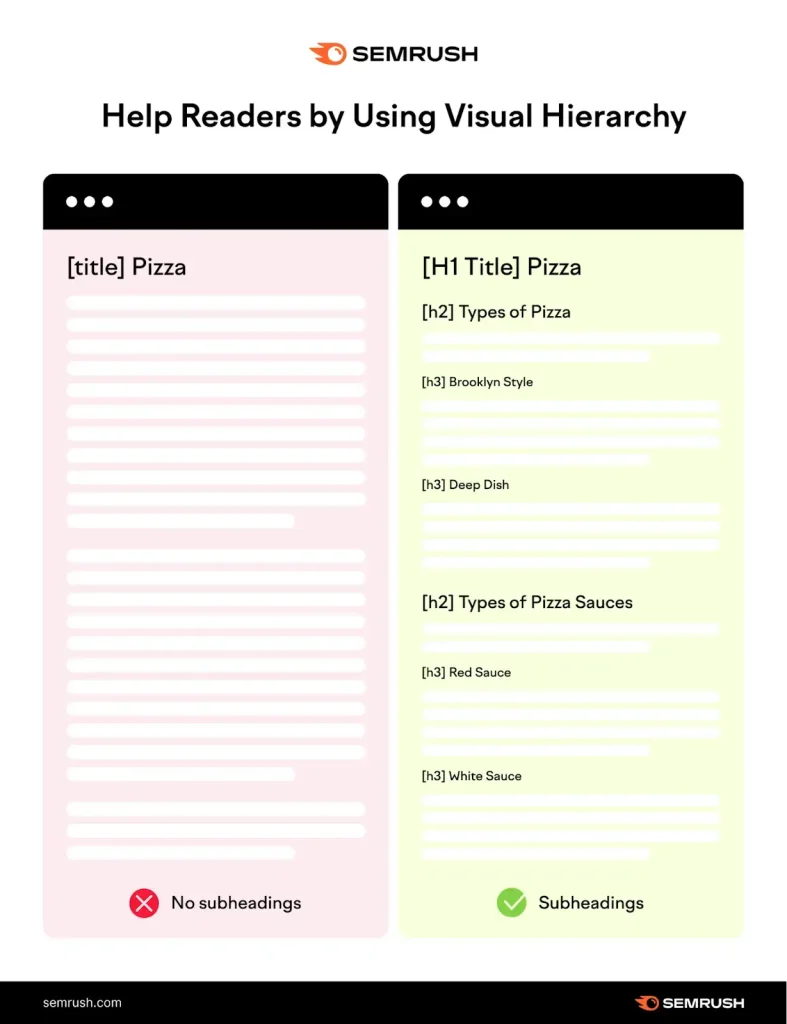
You can add different variations of keywords in headings so Google can have clear context about the page structure and information covered in the content. The H1 tag is used for the main page title, while other heading tags (H2, H3, H4) cover subtopics.
Also Read: All Types of Keywords in SEO With Examples (2025 Guide)
6. Build External Links
External links are links you get from high-authority websites to your website. These links build trust with the target audience and increase credibility of your site.
According to Google, external links to authoritative sources add value to users and boosts search engine rankings. Moreover, they enhance user experience, which is like a cherry on top.
Although most professionals focus on internal linking for on-page SEO, external links are among the top on-page SEO activities. When you link your content to trustworthy sites, it shows to Google that your page is reliable and credible. Also, it proves that your site is well-referenced.
Make sure to follow these tips while building external links:
- Use descriptive anchor text that appears naturally in content and shows to readers what they can expect when they click on the link.
- Link only to quality and authoritative sites related to your domain and topic.
- Check your site for any broken links or issues and fix them instantly.
- Avoid excessive use of external links; otherwise, it may look spammy.
7. Add Internal Links
Internal links are hyperlinks redirecting users to different pages on the same website. They help search engines find and understand the relationships between different web pages on your site.
Here are a few reasons why internal links are important for on-page SEO:
- Allow Google crawlers to find and navigate new pages.
- Help users navigate the website.
- Enable search engines to understand the structure of your website and how different pages are related.
- Shows Google that the linked page is valuable.
While adding internal links, here are a few points to remember:
- Place internal links strategically throughout the content. There must be a reasonable number of links on every page, and all of them must be contextually relevant and enhance user experience.
- Find relevant anchor texts that are used naturally in the content to add links. Anchor text must be descriptive and relevant to the page content you are linking to.
- Find the page that you want to link to but make sure it’s relevant and provide additional information related to the current topic.
8. Optimize Images Using Alt Tags
On-page SEO analysis also includes images, so you need to optimize them. Add images to the content to engage users and make it more attractive. Also, images are a crucial ranking factor and an effective way to increase online traffic. Optimize these images using descriptive alt text, which is HTML code to describe images on a web page. It serves two main purposes:
- Allow users with screen readers to hear image description
- Provide content to crawlers.
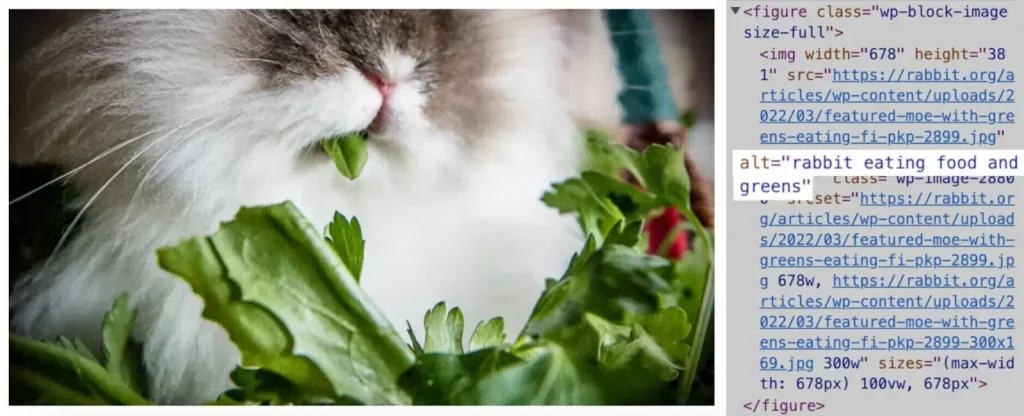

Here are a few tips for using alt text for images:
- Keep it brief and to-the-point
- Create a descriptive file name so search engines can understand the relevance of the image
- Don’t use alt text for decorative images, like horizontal page breaks.
- Add target keywords for better context
- Compress images using free tools for faster loading time
- Don’t mention ‘picture of’ or ‘image of’ as alt text itself is used to describe images.
Interview Questions for You to Prepare for Jobs
| Digital Marketing Interview Questions | SEO Interview Questions |
| Email Marketing Interview Questions | Content Writing Interview Questions |
On-Page SEO Elements
On-page SEO strategies include various elements that are majorly divided into three categories: content, HTML, and website architecture. We’ll discuss elements under each category in the following section:
- Keyword Research
- Visual Content
- SEO Content Writing
- Titles
- Headers
- Meta Description
- Image Alt Tags
- URL Structure
- Site Loading Speed
- Responsive Design
- Internal Linking
1. Content
Content elements include keyword research and how to incorporate relevant keywords into the content to yield the best results.
2. Keyword Research
The core of a high-quality content is finding relevant keywords and generating topics based on them. You can use different tools and software to conduct keyword research and determine search terms working for your competitors. List all the relevant keywords that you can target in your content.
During your keyword research, focus on the buyer’s journey, and user search intent. These factors can affect the way you use keywords and the type of content you create:
| Stages in a Buyer’s Journey | Recommended Website Pages |
| Awareness | Video, homepage, and blog posts |
| Consideration | Case studies, About Us page, Buyer’s guide |
| Decision | Comparison tools, Product demos, Product or pricing pages, Contact Us page |
Now that you have a list of keywords, it’s time to create keyword-rich content that answers users’ queries in simple and easy-to-understand language. Make sure to include keywords in search queries. Add them to your headings and main body to generate optimized content.
Make sure you know what your target audience is looking for, and then create content that meets their demands. Conduct in-depth research, so you don’t miss out on any opportunity.
3. Visual Content
Over 36% of users prefer visual search for online shopping. So, if you are still not adding visual content to your web pages, then you are missing out on great opportunities. Visual assets, such as images, videos, infographics, and charts can do wonders for your on-page SEO. Visual elements attract and engage visitors, provide a memorable user experience, and enhance your SEO efforts.
They make content easier to read and more scannable. Also, optimize images using alt tags to drive traffic from image search results. Adjust image size to avoid slow loading speed. Moreover, images must be shareable so you can explore more chances for backlinks.
Also Read: All Types of SEO (Search Engine Optimization): 2025 Guide
4. SEO Content Writing
Content is the king. Developing content that can engage the audience, attract search engines, and convert visitors into buyers is an exceptional skill. Writing innovative content and copies that adhere to search engine regulations and SEO best practices can be challenging. Although you can have hands-on training to master content marketing, here are a few points to remember:
Readability: Produce content that is easily readable and scanable so that users can easily find the information they are seeking.
Keep it brief: Have you ever visited a webpage or read content with lengthy sentences? Then you know how confusing and boring it can be. So, avoid repeating the same mistake and keep your sentences and paragraphs short and to the point.
Subheadings: Make your subheadings stand out by keeping them concise and eye-catching. Use multiple subheadings in your content to guide your readers.
Avoid Keyword Stuffing: Overusing or stuffing keywords is an unethical SEO practice that many SEO professionals use to boost the ranking of their content. However, Google doesn’t support this practice, and if it finds out about it, it can significantly hurt your search engine ranking.
Use Bullet Points: Bullet points give a proper structure to your content, breaking down information into smaller and understandable chunks. Use them to list points or whenever they make sense.
5. HTML
HTML elements are part of the source code, which you can see in the browser.
6. Titles
While generating titles for web pages, you need to pay attention to details. A title is a snippet of code, giving your content or page a title but it doesn’t play a significant role in SERP rankings. However, when combined with other critical on-page SEO elements, titles can show the relevance and context of the content.
Titles tell website visitors and search engines what they can expect to read and the information they will get after going through it. Your title must incude relevant keyword, which must appear naturally rather than looking forced.
7. Headers
Headers, or body tags, organize your content properly, so that the information you have provided on the page is divided into clear sections and subsections. They are the HTML elements <H1>, <H2>, <H3>, and so on, telling readers what the content is about. However, you need to write descriptive headings to convey the context and gist of each section so users can skip directly to the useful part.
Readers can determine the hierrachy of the web page using headers. Also, they help search engines understand the relevance of the content to keywords targeted. Heading tags also tell search engines about the most important and relevant parts of the entire content, so they can provide accurate search results based on search intent.
Search engines can display your page for more specific queries, which gives you more possibilities to appear on top of search engine rankings. You must remember that, unlike humans, search engines can’t identify headings based on weight and font size. Google sees content in the HTML format.
There are six major heading tags. While using content management systems like Squarespace and WordPress, you can see a drop-down menu of heading tags in the editor. You can customize the size of headings and apply them manually in the HTML code.
<H1>: It is the primary title of the page or blog. There is only one H1 tag on every page.
<H2>: H2 tags are used for the main sections of the content. An optimized content can have two to 22 H2 tags per page, depending on the length of the content. At least two H2 headings must include target keywords, which can be the first main section and conclusion.
<H3>: These are further labels used for writing different points in H2 sections. These are subheadings for H2 parts and must be used only when needed. Don’t force them into the content, and it’s not essential to include keywords in H3.
<H4> to <H6>: These headings don’t have much SEO value. So, if your content is short, these headings tags hardly make any sense and are not going to be readable.
8. Meta Description
A meta description is a short description of your web page that appears under the meta title on search engine result pages. It is like an ad for your web page because an informative and concise description ensures searchers that you have answered their queries, which compels them to click on the given link.
Many believe that meta description has nothing to do with SEO as it’s not one of the ranking factors. However, this is partly true because it may not be of much use in SEO strategies, but it offers two major benefits.
First, Google uses meta descriptions to understand what your page or content is about. Secondly, it affects click-through rates (CTRs). Also, a meta description helps users and searchers understand what a page offers, which leads to more clicks. So, no matter what anyone says, never ignore meta descriptions.
You can copy a meta description over to social media while sharing the content, which adds to clickthroughs. Here are a few points to consider while generating a meta description:
- It should be between 155-160 characters
- It should communicate accurate information
- It must be actionable
- It must include relevant keywords
Although you have to provide a meta description to Google, it may not use it every time. Search engines can dynamically create meta descriptions according to the content. So, make sure that you add heading tags in your article. This description is also shown on preview snippets, similar to what we see on social media.
9. Image Alt Text
Image alt text is the SEO for images, telling search engines the context and relevance of images you add on web pages. Optimizing images is now vital as Google and other search engines provide as many image-based results as text-based. You may work on various visual assets, but image optimization includes more technical aspects. The following tips will help you optimize image alt text:
- Customize each file name rather than using a generic name
- Create SEO-friendly alt tags
- Add mobile-friendly images
- Select the right format and size for faster page loading
10. Site Architecture
The architecture of a website includes all the elements combined together to create a website and web pages. The structure of a site enables users and search engines to crawl pages and content easily. Here are the elements included in the site architecture:
11. URL Structure
It was not long ago that Google stressed a page’s URL for higher rankings. It was a leading factor in SEO, and marketers meticulously chose keywords to include in the web address to boost search engine rankings. However, Google’s algorithm changed, and this crucial element now plays a small role in SEO.
Still, URLs can affect your overall SEO score and your site’s initial search engine ranking. Marketers suggest that URLs are important to group pages, so even if they are not the priority, you can’t ignore them completely.
URLs must be simple for readers and search engines to read. Also, they are critical in building a consistent hierarchy of blog posts, web pages, and other internal pages. URLs can be a series of numbers or a title you choose. Sometimes, content management systems build the URL automatically for your web pages. You can edit this URL to replace spaces with dashes, make it short and precise, and add target keywords.
Also Read: Top 7 Free Backlink Checker Tools in 2025 (Check Backlinks)
12. Site Loading Speed
A slow and unresponsive website can hurt more than your business’ online reputation. It frustrates users and hampers your search engine ranking too. So, make sure your website loads within 3-4 seconds, whether it’s on mobile or desktop. It is a vital element to make on-page SEO work. Google and other search engines consider page loading speed and user experience while listing search engine results.
Moreover, a site that loads slowly or haphazardly can struggle with engaging users. Visitors will not stick around for long, which will impact ROI and conversions. The minimum loading speed a website needs to meet is changing constantly. So, keep a close eye on the latest parameters and meet the standards by working continuously on your site.
Here are a few steps you can take to improve page loading speed:
- Optimize images
- Enable compression
- Use browser cache
- Reduce redirects
Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool to check the page loading speed of your site.
13. Responsive Design
In 2016, mobile search volume peaked, surpassing desktop searches for the first time ever. In the following years, mobile searches witnessed only growth, currently accounting for over 56% of total internet usage with tablets contributing to another 2.4%.
With users relying more and more on their smartphones to search for queries, Google opted for the logical path and started favoring websites with responsive designs for mobile search rankings. This update affects only mobile searches. Although websites without responsive designs can still possibly rank for mobile searches, Google highly recommends businesses launch mobile-friendly sites.
The design, content layout, and images must be navigable on mobile devices. To check the compatibility of your website with smartphones, you can use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool.

14. Internal Linking
Internal linking refers to the process of adding hyperlinks to different pages on your website. It helps search engines understand relationships between multiple web pages, and users can navigate the website easily. It is an important SEO element as it sends readers to other useful pages on the website, which engages them with your content for longer and shows that your site is helpful and valuable.
The longer visitors are on your website, the more time search engines have to crawl and index pages. This will enable crawlers to find more information about the site, which will boost its search engine ranking.
However, not all inbound links are helpful, as some links from guestbooks, forums, etc., can be fake with the goal of cheating the ranking systems. A few important factors to add internal links are:
Identify the Target Page: Decide the web page on your website to link. Make sure that the selected web page is relevant and offers valuable and additional information regardingthe published content.
Add Anchor Text: Find the anchor text, which is clickable, to use for internal links. They should appear naturally in the content and must be related to the content of the page you are linking to.
Place Links Strategically: Select a reasonable number of links for each page. These links must be contextually relevant and enhance user experience. Avoid adding excessive links; otherwise, it can lead to spammed links.
Conclusion
On-page SEO is key to accelerating business growth and boosting search engine rankings. Hope this blog helped you understand the concept of on-page SEO and find answers to common queries. By focusing on different on-page aspects and elements, you can move up on SERPs, improving your website’s exposure and credibility in the digital environment.
Read more blogs: