Web development is the process of creating websites and web applications that run on the internet. It involves building the structure of web pages, designing how they look, adding interactive features, and writing backend code to handle data and application logic. From simple personal websites to large platforms like online stores and social media sites, web development plays an important role in today’s digital world. Every website viewed in a browser is created and maintained by web developers.
This web development roadmap is a clear, step-by-step guide created to help beginners learn web development in the right order. It explains what to learn first, what to learn next, and how different skills connect with each other. By following this roadmap, learners can avoid confusion, stay focused, and gradually build the skills needed to become confident and job-ready web developers.
Who is a Web Developer?
A web developer is a professional who builds and maintains websites and web applications. They turn ideas and designs into functional websites using programming languages, tools, and frameworks. Web developers make sure websites work properly, load fast, and provide a good user experience on different devices.
Web developers work on both the frontend and backend of a website. Frontend developers focus on design and interactivity, while backend developers handle servers, databases, and logic. Some developers work as full-stack developers and manage both sides of web development.
Key Responsibilities of a Web Developer
- Create and maintain websites and web applications
- Write clean and efficient frontend and backend code
- Ensure websites are responsive and user-friendly
- Connect websites to databases and APIs
- Fix bugs and improve website performance
- Maintain website security and updates
Types of Web Developers
Web developers are classified based on the part of the website they work on. Some developers focus on designing and building the user interface, while others manage the server, database, and application logic. There are also developers who handle both frontend and backend tasks in a single role. Below are the main types of web developers mentioned:
- Frontend Developer: Works on the part of the website that users see and interact with in a browser. This role focuses on layout, design, and user experience. HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are used to build attractive and interactive web pages.
- Backend Developer: Handles the server-side functionality of a website, including data processing, database management, server logic, and user authentication.
- Full-Stack Developer: Covers both frontend and backend development. This role works on the complete web application, from creating user interfaces to handling servers and databases.
Why Choose Web Development as a Career?
Web development is a popular career because it offers strong demand, good salaries, and many job opportunities. Almost every business today needs a website or web application, which means skilled web developers are always needed across different industries.
Another reason to choose web development is flexibility. Developers can work in companies, freelance, or even work remotely from anywhere. The field also encourages continuous learning, as new tools and technologies keep web development interesting and future-ready.
Web development also provides long-term career growth and job stability. Many beginners often wonder, Is Web Development a Good Career? Yes, it is a strong choice because web development skills are in high demand. With regular practice and the right skills, anyone can build a successful and secure career in this field.
Recommended Professional Certificates
Full Stack Development Mentorship Program
WordPress Bootcamp
Web Development Roadmap 2026: Step-by-Step
This web development roadmap provides a clear, step-by-step learning path that helps beginners and professionals understand what to learn, the correct order to follow, and how different skills connect with each other.
Below are the steps that help you become a skilled web developer:
- Basics of the Internet and How the Web Works
- Choosing the Right Technology Stack
- Learn HTML (Structure of Web Pages)
- Learn CSS (Styling and Layouts)
- Responsive Web Design
- Learn JavaScript (Logic and Interactivity)
- Version Control with Git and GitHub
- Frontend Frameworks
- Mastering Backend Development
- Databases
- Building the Final Web Application
- Deployment and Hosting
- Testing, Debugging, and Optimization
- Prepare for Web Developer Jobs and Interviews
Now, we will go through each step one by one to clearly explain what you should learn, which key concepts to focus on, and how each step helps you grow into a confident and job-ready web developer.
Step 1: Basics of the Internet and How the Web Works
This step helps you understand how the internet works before you start building websites. You learn what the internet is, how websites are accessed, and how browsers request information from servers. It also explains the role of domains and how users reach websites using web addresses.
You also learn basic concepts like DNS, HTTP, and HTTPS, which control how data moves between browsers and servers. Understanding these topics helps you know how web pages load and prepares you for frontend and backend development in the next steps.
Step 2: Choosing the Right Technology Stack
Choosing the right technology stack helps decide which tools are used to build a web application. It includes selecting frontend frameworks, backend technologies, and databases. The right stack depends on project needs, career goals, and job demand, making learning smoother and more focused.
- MERN Stack: MERN is a popular stack that uses MongoDB for data storage, Express and Node.js for backend development, and React for building user interfaces. It is widely used for modern, fast, and scalable web applications.
- MEAN Stack: MEAN includes MongoDB, Express, Node.js, and Angular for frontend development. This stack is commonly used for large, structured, and enterprise-level web applications.
The time needed to learn web development depends on your background, practice level, and learning goals.
- Beginner Level (2–3 months): Learn basic web concepts and core skills like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Intermediate Level (4–6 months): Practice frontend frameworks, backend basics, databases, and API integration.
- Advanced Level (3–5 months): Focus on advanced backend concepts, performance optimization, security, and real-world projects.
Regular practice and hands-on projects help speed up learning and build real confidence.
Step 3: Learn HTML (Structure of Web Pages)
After choosing the right technology stack, it is important to learn HTML because it is a core part of web development. HTML is used to structure web pages and helps browsers understand, organize, and display content correctly. A strong understanding of HTML is required before moving on to styling or adding interactivity.
- HTML Basics: Learn essential concepts such as tags, elements, attributes, headings, paragraphs, links, images, lists, tables, and the basic structure of a web page.
- Semantic HTML: Use meaningful tags like header, section, article, and footer to improve page structure, accessibility, and search engine optimization.
- HTML Forms: Create HTML forms to collect user input using input fields, labels, buttons, and basic validation attributes.
- HTML5 Features: Understand modern features such as audio, video, canvas, local storage, and new semantic elements used in modern websites.
Mastering HTML gives you a strong foundation for CSS and JavaScript, helping you build well-structured, accessible, and modern web pages with confidence.
Step 4: Learn CSS (Styling and Layouts)
After learning HTML, learning CSS is essential for styling and designing web pages. CSS controls the visual appearance of a website, including colors, fonts, spacing, alignment, and overall layout. It transforms simple HTML content into clean, attractive, and user-friendly web pages.
- CSS Basics: Learn how selectors, properties, and values work, along with colors, fonts, text styling, backgrounds, borders, margins, and padding.
- Box Model: Understand how content, padding, borders, and margins affect the size and spacing of elements on a page.
- Layouts: Learn modern layout systems like Flexbox and Grid to arrange content in rows, columns, and sections.
- Positioning: Understand static, relative, absolute, fixed, and sticky positioning to control element placement.
- CSS Reusability: Learn how to write clean, organized, and reusable CSS for better maintainability.
Mastering CSS helps you create attractive, responsive, and professional-looking websites that work smoothly across all devices.
Step 5: Responsive Web Design
Responsive web design helps websites adjust automatically across different screen sizes and device types, including mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and desktop computers. It ensures users get a smooth and consistent experience no matter how they access a website. Responsive design is an essential skill for modern web developers.
- Mobile-First Approach: Start designing for small screens first and then enhance the layout for larger screens. This improves performance and usability on mobile devices.
- Flexible Layouts: Use flexible grids, percentages, and responsive units like em, rem, and vh/vw instead of fixed widths to create adaptable layouts.
- Media Queries: Apply CSS rules based on screen size, resolution, and orientation to adjust layouts, fonts, and spacing.
- Responsive Images: Use scalable images and modern formats to ensure images load properly without slowing down the website.
Learning responsive web design helps you build modern, user-friendly websites that look good and work well on all devices.
No Masterclass found!
Step 6: Learn JavaScript (Logic and Interactivity)
JavaScript is an essential programming language used to add logic and interactivity to websites. It allows web pages to respond to user actions such as clicks, form submissions, and keyboard input. Learning JavaScript helps you turn static web pages into dynamic and interactive applications.
- JavaScript Basics: Start with variables and constants, data types, operators, conditions, loops, and functions. These basics help you write simple programs and control how your website behaves.
- DOM Manipulation: Learn how JavaScript interacts with HTML and CSS through the Document Object Model. This allows you to update content, change styles, and create interactive elements in real time.
- Events and User Interaction: Handle user actions like clicks, hover effects, and form inputs to improve user experience.
- Asynchronous JavaScript: Understand concepts like callbacks, promises, and async/await to work with APIs and load data without refreshing the page.
- JavaScript Best Practices: Learn clean coding practices, error handling, and debugging to write efficient and maintainable code.
Mastering JavaScript prepares you for frontend frameworks and backend development, helping you build powerful and interactive web applications with confidence.
Step 7: Version Control with Git and GitHub
Version control helps track changes in code and makes collaboration easier and safer. Git allows you to manage source code locally, while GitHub provides a platform to store, share, and collaborate on projects. Learning Git and GitHub is essential for professional web development and team-based workflows.
- Git Basics: Learn how Git works, including repositories, commits, branches, merges, and the standard workflow used to manage and organize source code.
- Tracking Changes: Use commands like add, commit, and status to monitor and save code changes.
- Branching and Merging: Create separate branches to work on new features safely and merge them back into the main code without disrupting existing functionality.
- GitHub Repositories: Host projects online, manage files, and maintain version history.
- Collaboration: Work with other developers by sharing code, reviewing changes through pull requests, and managing tasks using issues and project boards.
- Undo and Recovery: Revert changes, fix mistakes, and recover previous versions safely.
Understanding Git and GitHub helps you manage projects efficiently, collaborate confidently, and maintain clean, organized code throughout development. You can also use other reliable version control platforms such as GitLab, Bitbucket, Mercurial, and Apache Subversion based on project or team needs.
Step 8: Frontend Frameworks
Frontend frameworks are used to build modern, fast, and interactive user interfaces. They help developers write less repetitive code and manage large applications more easily. Using a frontend framework improves development speed and makes applications easier to maintain and scale.
- Popular Frontend Frameworks: Learn widely used frameworks such as React, Angular, or Vue. These frameworks are in high demand and are used to build real-world web applications.
- Component-Based Architecture: Understand how to divide the user interface into small, reusable components. This makes code cleaner, reusable, and easier to manage.
- State Management: Learn how to handle application data, user actions, and UI updates efficiently using state and props.
- Routing and Navigation: Learn how to manage page navigation within a single-page application without refreshing the browser.
- Performance Optimization: Understand techniques like lazy loading and code splitting to improve application speed.
Learning frontend frameworks helps you build professional, scalable, and user-friendly web applications. If you want to explore frameworks in detail, you can check out this web development frameworks guide to understand popular tools and their real-world use.
Step 9: Mastering Backend Development
As you move ahead in web development, backend development becomes a key area to focus on. It handles how data is processed, stored, and delivered to users. Backend development connects the frontend with servers and databases, ensuring features like login, data storage, and user actions work correctly. It plays a vital role in building secure, scalable, and reliable web applications used in real-world projects.
Choosing a Backend Programming Language
Select a backend language that is widely used, beginner-friendly, and suitable for building scalable web applications.
- Python: Easy to learn and known for its clean and readable syntax. It offers powerful frameworks and libraries that help build secure, efficient, and maintainable backend systems. Python is also widely used beyond web development.
- NodeJS: Allows JavaScript to run on the server side. It is fast, scalable, and well-suited for handling multiple user requests. Using JavaScript for both frontend and backend simplifies full-stack development.
Learning CLI (Command Line Interface)
The command line is an essential tool for backend developers. It helps manage projects, run servers, install dependencies, and automate tasks efficiently during development.
- Run backend servers
- Install and manage packages
- Work with Git repositories
- Execute scripts and commands
Learning APIs
APIs enable the frontend and backend to communicate by exchanging data. Learning APIs helps you send requests, receive responses, and integrate external services securely. APIs are essential for building modern, connected web applications.
- RESTful API
- JSON API
Mastering backend development prepares you to build complete, secure, and scalable web applications and grow as a backend or full-stack web developer.
Step 10: Learn Databases to Store and Manage Data
Databases are used to save, organize, and access data for web applications. They store important information such as user details, posts, orders, and application records. Without databases, websites cannot handle or display dynamic content.
In this step, you learn how databases function and how backend applications work with them. You also understand the basic actions needed to manage data, including adding new records, viewing stored information, making updates, and removing data when required.
Types of Databases
- SQL Databases: Store information in structured tables organized by rows and columns. Examples include MySQL and PostgreSQL.
- NoSQL Databases: Store data in flexible formats like documents. MongoDB is a common example.
Database Operations
These operations allow applications to manage data efficiently. They are used to add new information, retrieve stored records, update existing data, and remove unwanted data from the database.
- Create: Add new records to the database.
- Read: Retrieve existing data from the database.
- Update: Modify stored data when changes are needed.
- Delete: Remove unwanted or outdated records.
Database Design
Database design focuses on organizing data in a clear and structured way. Good design improves performance, reduces duplication, and ensures data accuracy, making applications easier to manage and scale.
Learning databases helps you build dynamic, data-driven web applications and is essential for backend and full-stack development.
Explore More Career Roadmaps
Step 11: Building the Final Web Application
Building the final web application is the stage where all your learning comes together in one complete project. At this step, the focus is on creating a fully functional application by combining frontend design, backend logic, and database management. This process helps you understand how real-world web applications are planned, built, and maintained.
- Project Planning and Structure: Begin by defining the application goal, target users, core features, and user flow. Plan the folder structure, pages, and data flow to keep development organized and efficient.
- Frontend Development: Build clean and user-friendly interfaces with proper layouts, styling, and interactive elements. Focus on usability, smooth navigation, and consistent design.
- Backend Implementation: Develop server-side logic to handle requests, process data, manage authentication, and control application behavior.
- Database Integration: Design and connect databases to store user data, content, and application settings securely.
- API Communication: Use APIs to connect frontend and backend, enabling dynamic data exchange and real-time functionality.
- Authentication and Authorization: Set up secure user login, registration, and role-based access control to ensure only authorized users can access protected data and features.
- Error Handling and Validation: Handle invalid inputs and unexpected issues to ensure application stability and reliability.
- Code Organization: Keep code clean, modular, and well-structured to simplify future updates and maintenance.
Building a complete web application improves practical skills, strengthens problem-solving ability, and prepares you for professional web development work with confidence.
Web Development Projects
When building your final web application, the goal is to apply all your skills in one real-world project. This helps you understand full-stack development and strengthens your portfolio for jobs or internships.
Project Ideas for Your Final Web Application:
- E-commerce Platform: Build an online shopping website with product listings, user accounts, cart functionality, and order management. This project helps you learn payments, databases, and authentication.
- Social Media Network: Create a platform where users can register, post content, like, comment, and follow others. This improves your understanding of user interaction, real-time updates, and backend logic.
- Task Management Application: Develop an app to create, update, and track tasks. It helps you practice CRUD operations, user roles, and clean UI design.
- Online Learning Platform: Build a website for courses, lessons, and user progress tracking. This project teaches data handling, user access control, and scalable design.
Completing any one of these projects gives you hands-on experience and shows that you can build a complete, working web application from scratch. If you want to explore more, you can check web development project Ideas, which include source code and clear explanations to help you learn better.
Step 12: Deployment and Hosting
After creating projects, the next step is to make your web application live so users can access it online. Deployment and hosting help you understand how applications are published on the internet and made available to real users. Key Areas to Learn in Deployment and Hosting:
- Hosting Platforms: Learn to deploy applications on popular platforms such as Netlify, Vercel, AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Heroku, and DigitalOcean.
- Frontend and Backend Deployment: Understand how frontend and backend applications are deployed, either separately or together.
- Domain Setup: Connect a custom domain to your application using services like GoDaddy, Namecheap, or Cloudflare.
- Server Configuration: Set up environment variables, ports, build commands, and runtime settings required to run applications correctly.
- Production Builds: Prepare optimized production builds before deployment.
- Application Updates: Upload changes and improvements while keeping the application accessible to users.
- Rollback Basics: Learn how to restore a previous working version if deployment issues occur.
Learning deployment and hosting helps you publish projects professionally and understand how web applications run in real production environments.
Step 13: Testing and Monitoring
Testing and monitoring play an important role in maintaining the quality, stability, and reliability of a web application. Proper testing helps identify problems early, while monitoring ensures the application continues to perform well after deployment. Together, they help prevent user-facing issues and improve overall application health.
Software Testing
Testing focuses on checking whether the application works as expected under different conditions. Common testing approaches include:
- Unit Testing: Tests individual functions or components separately to ensure each part works correctly.
- Integration Testing: Verifies that different modules or services work together without issues.
- End-to-End Testing: Tests complete user flows from start to finish to simulate real user behavior.
- Performance Testing: Evaluates application speed, response time, and behavior under heavy traffic.
- Security Testing: Identifies weaknesses and vulnerabilities to protect data and prevent unauthorized access.
Monitoring Application Performance
Monitoring helps track the application’s behavior in real time and ensures smooth operation.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracks response time, server load, and error rates to detect slowdowns.
- Availability Monitoring: Ensures the application remains online and accessible to users.
- Logging and Error Tracking: Records system events and errors to help diagnose problems quickly.
- Alerts and Notifications: Sends alerts when issues occur, allowing faster resolution.
- Scalability Monitoring: Observes resource usage to support growth and handle increased traffic.
Learning testing and monitoring helps maintain high-quality applications, reduce downtime, and deliver a reliable experience to users.
Step 14: Prepare for Web Developer Jobs and Interviews
Preparing for web developer jobs involves strengthening your core development skills and understanding industry expectations. Focus on improving HTML, CSS, JavaScript, frontend frameworks, backend development, databases, and deployment while practicing with real-world projects and problem-solving scenarios.
Build a strong portfolio that showcases your best web development projects, clean code, responsive designs, and complete full-stack applications. Practice common interview questions, coding challenges, system basics, and project explanations to improve confidence and communication during interviews.
You can explore our full-stack development course to learn web development in a structured way. This program offers step-by-step guidance, real-world projects, expert mentorship, and job-ready skills to help you confidently start your web developer career.
Web Development Career Guides
| How to Become a Web Developer? | What does a Web Developer do? |
| Is Web Development a Good Career? | How to Become Frontend Developer? |
| How to Become Backend Developer? | How to Become Full Stack Developer? |
Career Opportunities After Completing Web Development
After completing the web development roadmap, many career paths open across tech industries, startups, and freelance platforms, offering growth, flexibility, and strong earning potential.
- Frontend Developer: Focuses on building user interfaces and user experiences using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks. This role ensures websites look good, work smoothly, and are easy to use across devices.
- Backend Developer: Handles server-side logic, databases, APIs, and authentication. Ensures data is processed securely and efficiently while supporting frontend functionality in real-world web applications.
- Full-Stack Developer: Manages both frontend and backend development. This role is ideal for building complete web applications independently and is highly valued by startups and fast-growing companies.
- Web Application Developer: Builds dynamic and interactive web applications such as dashboards, portals, and SaaS platforms, focusing on performance, scalability, and real-world business requirements.
- Freelance Web Developer: Works independently on client projects, offering website development, maintenance, and customization services. This role provides flexibility, remote work options, and income based on skills and experience.
Web development skills offer long-term career growth, global job opportunities, and the ability to build real products used by people every day.
Web Developer Salary and Demand in 2026
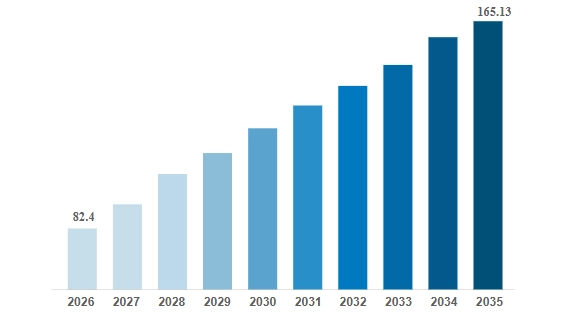
The global web development market is projected to be worth around USD 82.4 billion in 2026 as businesses boost their online presence and digital services. This market is expected to grow steadily, reaching about USD 165.13 billion by 2035 at a CAGR of 8.03 percent. This strong growth reflects ongoing investments by companies in websites, web apps, and interactive web platforms.
Demand for web developers is rising worldwide because websites and web applications are critical for business success, customer engagement, and e-commerce growth. Over 60 percent of companies are increasing their focus on online services, which expands job opportunities for web developers who can build responsive, user-friendly, and data-driven solutions.
Web Developer Salary in India
| Experience Level | Average Salary Range |
| Fresher / Entry (0–2 yrs) | ₹3 – ₹5 LPA |
| Mid-Level (2–5 years) | ₹5 – ₹10 LPA |
| Senior (5+ yrs) | ₹10 – ₹18+ LPA |
Salary Influencing Factors:
- Experience and Skills: Practical skills and real project experience often lead to higher pay.
- Company and Industry: Larger technology firms and product companies may offer better compensation.
- Location: Major cities often have higher salary ranges than smaller regions.
Web development continues to be in high demand as companies worldwide invest in strong online platforms. With continuous market growth, career opportunities and competitive salaries make web development a rewarding and future-ready career choice in India for 2026 and beyond.

FAQs About Website Development Roadmap
A web development roadmap is a step-by-step learning plan that shows what skills you should learn, in what order, and why. It helps you avoid confusion, stay focused, and progress from basics to advanced concepts confidently.
Yes, the web development roadmap is suitable for beginners because you start with simple concepts like HTML and CSS. You learn step by step, avoid confusion, and build confidence as you gradually develop real-world web development skills.
The time depends on your learning pace and practice. If you study consistently, you can follow a complete web development roadmap in 6 to 9 months while building projects and strengthening practical, job-ready skills.
No, you do not need a degree to become a web developer. You can learn skills through the web development roadmap, online courses, practice projects, and self-study. Employers value practical skills, portfolios, and problem-solving ability more than formal education today world.
In a roadmap to learn web development, you should start with HTML, CSS, and basic JavaScript. These fundamentals help you understand structure, styling, and interaction before moving to frameworks, backend tools, and databases.
Yes, website development and app development are different. Website development focuses on building applications that run in web browsers, while app development targets software installed on devices. Each follows different design approaches, workflows, and user interaction patterns.
Yes, after completing the web development roadmap for beginners and building projects, you can apply for entry-level roles. Employers value practical skills, portfolios, and problem-solving ability more than just certificates or theoretical knowledge.
You can start by learning the basics of both frontend and backend. Later, choose frontend, backend, or full-stack based on your interest. The web developer roadmap helps you explore all paths before specializing.
Projects are very important because they help you apply what you learn. Building real projects improves confidence, problem-solving skills, and portfolio strength, making it easier for you to explain your abilities during interviews.
Yes, web development is a good career in 2026 because the demand for skilled developers continues to grow. You can work in companies, freelance, or remote roles, earn well, and build real products used by people across the world.
Start Learning With Our Free Tutorials





Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Comments (0)
No comments yet.