Data science is the field of finding useful insights from data to help businesses and organizations make better decisions. It combines data analysis, statistics, programming, and problem-solving skills. A data scientist works with large datasets, cleans data, finds patterns, and turns raw information into meaningful results. With growing digital data, data science has become one of the most in-demand and future-ready career fields. A clear data scientist roadmap helps beginners understand how data science skills connect and how real-world problems are solved using data.
This Data Science roadmap explains the step-by-step path to becoming a skilled data scientist. It explains what skills to learn, in what order, and why each step matters. From basics like math and Python to advanced topics like machine learning and deployment, this roadmap helps you build confidence and grow job-ready skills in a structured way.
Who is a Data Scientist?
A data scientist is a professional who collects, analyzes, and explains large amounts of data to solve real-world problems. They use statistics, programming, and logical thinking to find meaningful patterns and trends hidden in data.
Data scientists help organizations make smarter decisions by turning raw data into clear insights. They work across industries such as healthcare, finance, education, and technology to improve products, services, and business strategies.
Key Responsibilities of a Data Scientist
- Collect, clean, and organize large datasets from multiple structured and unstructured data sources
- Analyze data using statistical techniques to identify trends, patterns, and valuable insights
- Build machine learning models to predict outcomes and support data-driven decision-making
- Visualize data using charts and dashboards for easy understanding by non-technical users
- Collaborate with teams to solve problems and deliver practical, data-based solutions
Why Choose Data Science as a Career?
Data science is a strong career choice because it offers high demand and long-term job stability. Almost every industry relies on data to make better decisions, which creates steady demand for skilled data scientists worldwide. This demand keeps growing as data generation increases.
Another reason to choose data science is its excellent salary potential and clear career growth path. Data scientists usually receive higher pay than many other technology roles. With experience, you can move into senior, lead, or specialized roles like machine learning engineer or data architect.
Data science also offers diverse and meaningful work opportunities. You solve real business problems, use modern tools, and keep learning new technologies. Your work directly helps improve products, services, and customer experiences, making this career both rewarding and future-ready.
Recommended Professional Certificates
Data Analytics Mentorship Program
Data Science & AI Mentorship Program
Data Scientist Roadmap 2026: Step-by-Step Learning Guide
Below are the steps that help you become a skilled data scientist:
- Understand the Basics of Data and Analytics
- Learn Mathematics and Statistics for Data Science
- Master Python for Data Science
- Learn SQL and Data Handling
- Learn Data Cleaning and Data Preparation
- Learn Data Visualization and Storytelling
- Perform Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Learn Machine Learning Fundamentals
- Learn Advanced Machine Learning Techniques
- Understand Deep Learning and AI Basics
- Work with Big Data and Cloud Platforms
- Build Real-World Projects and a Data Science Portfolio
- Learn Model Deployment and MLOps Basics
- Prepare for Data Scientist Jobs and Interviews
Now, we will go through each step one by one to clearly explain what you should learn, which key concepts to focus on, and how each step helps you grow as a data scientist in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
Also Read: Data Science Course Syllabus: Fees, Duration, Eligibility, Details (With PDF)
Step 1: Understand the Basics of Data and Analytics
This step builds the foundation of your data science journey. You learn what data is, how it is collected, and how analytics turns raw information into meaningful insights that support better decision-making across industries. Below are the key concepts to focus on.
- What Is Data: Understand structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, along with common data types such as numerical, categorical, and text data.
- Types of Analytics: Learn descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, and how each type answers different business questions.
- Common Data Types: Learn numerical, categorical, ordinal, binary, time-series, and text data used in data science projects.
- Data Collection Sources: Understand where data comes from, such as databases, surveys, sensors, websites, and application logs.
Understanding these basics helps you think analytically and build a strong foundation for learning advanced data science concepts in the next steps of the data scientist roadmap.
Step 2: Learn Mathematics and Statistics for Data Science
Mathematics and statistics are essential for understanding how data science works. They help you analyze data correctly, measure uncertainty, and identify patterns that support data-driven decision-making.
These concepts also form the base of machine learning models. A strong understanding of mathematics and statistics improves your ability to work with real-world data and build reliable data science solutions.
- Linear Algebra Basics: Learn vectors, matrices, matrix operations, and linear equations used in data science algorithms.
- Probability Fundamentals: Understand probability, random variables, conditional probability, and basic probability rules.
- Statistical Measures: Learn mean, median, mode, variance, standard deviation, and correlation to summarize data.
- Data Distributions: Study normal, binomial, and Poisson distributions commonly used in data analysis.
- Hypothesis Testing: Learn confidence intervals, p-values, and basic hypothesis testing for data-driven conclusions.
Understanding these concepts strengthens your analytical skills and prepares you for advanced data science techniques.
Upcoming Masterclass
Attend our live classes led by experienced and desiccated instructors of Wscube Tech.
Step 3: Master Python for Data Science
Once you have a basic understanding of mathematics and statistics, Python helps you apply those concepts in real data science projects. Python is one of the most important tools in data science because it is easy to learn, powerful, and widely used for data analysis, automation, and machine learning tasks across industries. Below are the key concepts that help you master Python for data science.
- Python Basics: Learn Python variables, Python data types, Python conditional statements, Python loops, Python functions, and basic programming concepts to write clean and readable code.
- Working with Libraries: Use NumPy for numerical operations and Pandas for data cleaning and analysis.
- Data Visualization: Learn Matplotlib and Seaborn to create charts, graphs, and plots that help you understand patterns and trends in data.
- Data Handling: Read, clean, transform, and process data from CSV, Excel, JSON, and other common file formats.
- Python for Machine Learning: Use Scikit-learn to build, train, test, and evaluate machine learning models efficiently.
Mastering Python gives you the confidence to work with data, turn ideas into useful solutions, and apply data science skills effectively while solving real-world problems.
Step 4: Learn SQL and Data Handling
SQL is a core skill for every data scientist because most real-world data is stored in databases. Learning SQL helps you efficiently access, filter, combine, and manage large datasets. Strong data handling skills ensure your analysis is accurate and reliable. Below are the key areas to focus on.
- SQL Basics: Learn database concepts, tables, rows, and columns, along with core queries such as SELECT, WHERE, ORDER BY, and GROUP BY.
- Data Filtering and Sorting: Use SQL conditions to filter records and sort data based on business needs.
- Joins and Relationships: Learn INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, and RIGHT JOIN to combine data from multiple tables.
- Aggregations: Use functions such as COUNT, SUM and AVG to calculate totals and averages, and MIN and MAX to find the smallest and largest values in data.
- Data Handling Skills: Clean, update, and maintain data to ensure accuracy and consistency across databases.
Learning SQL and data handling allows you to work smoothly with structured data, prepare reliable datasets, and perform accurate analysis required in real-world data science projects.
Step 5: Learn Data Cleaning and Data Preparation
Data cleaning and preparation are important steps in the data science process because real-world data is often incomplete, inconsistent, or messy. Before any meaningful analysis or modeling, data must be cleaned and properly prepared to ensure accurate results. This step helps you improve data quality and make datasets ready for analysis and machine learning.
- Handling Missing Data: Learn techniques to identify, remove, or fill missing values using suitable methods.
- Dealing with Outliers: Understand how to detect and handle outliers that can distort analysis results.
- Data Formatting: Convert data into correct formats, such as dates, numbers, and categories.
- Data Transformation: Normalize, scale, and encode data to make it suitable for analysis and models.
- Data Validation: Check data consistency and correctness to avoid errors in later stages.
Learning data cleaning and preparation helps you create high-quality datasets, reduce errors, and build a strong base for accurate analysis and reliable data science solutions.

Step 6: Learn Data Visualization and Storytelling
Data visualization and storytelling help you communicate insights clearly and effectively. A data scientist must not only analyze data but also present results in a way that is easy to understand for both technical and non-technical audiences.
- Visualization Basics: Learn how to choose the right charts, such as bar charts, line charts, pie charts, and histograms, for different data types.
- Data Visualization Tools: Use tools like Matplotlib, Seaborn, Power BI, or Tableau to create clear and meaningful visuals.
- Storytelling with Data: Learn how to explain insights using visuals, context, and simple language to support decision-making.
- Design Principles: Understand color usage, labels, and layout to make visuals clean and readable.
- Dashboards and Reports: Create dashboards and reports that summarize key insights and trends.
Strong data visualization and storytelling skills help you turn complex data into clear messages that drive better decisions.
Step 7: Perform Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Exploratory Data Analysis is the process of understanding data by examining its structure, patterns, and behavior. It involves analyzing datasets using summary statistics and visualizations to identify trends, relationships, missing values, and outliers. EDA helps data scientists gain meaningful insights, understand data quality, and develop a clear understanding of the information before applying advanced techniques.
Step 8: Learn Machine Learning Fundamentals
After learning Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA), it is time to move into machine learning. Machine learning is a core part of data science that enables systems to learn from data and make predictions without explicit programming. Understanding these fundamentals helps you build models that solve real-world problems effectively. Below are the key areas to focus on.
- Machine Learning Basics: Learn what machine learning is, how it works, and the differences between supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised learning.
- Common Algorithms: Understand algorithms such as linear regression, logistic regression, decision trees, k-nearest neighbors, and k-means clustering.
- Model Training and Testing: Learn how to split data into training and testing sets and evaluate model performance.
- Evaluation Metrics: Study accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and the confusion matrix to measure results.
Overfitting and Underfitting: Learn how to balance model complexity to improve performance on new data.
Learning the fundamentals of machine learning enables you to build reliable predictive models, solve complex data challenges, and confidently progress toward advanced data science and AI.
Step 9: Learn Advanced Machine Learning Techniques
Once you understand machine learning fundamentals, the next step is to explore advanced techniques that improve model accuracy and handle complex data problems. Advanced machine learning helps you work with large datasets, capture non-linear patterns, and build more powerful predictive systems. Below are the key areas to focus on.
- Ensemble Methods: Learn techniques like Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, and XGBoost to combine multiple models for better performance.
- Advanced Algorithms: Study Support Vector Machines (SVM), Naive Bayes, and k-means variants for specialized use cases.
- Feature Engineering: Learn how to create, select, and transform features to improve model results.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Understand grid search and random search to optimize model performance.
- Model Optimization: Learn cross-validation and regularization techniques to reduce overfitting.
Learning advanced machine learning techniques helps you build robust, high-performing models and prepares you for real-world data science projects and AI applications.
Explore More Career Roadmaps
Step 10: Understand Deep Learning and AI Basics
Deep learning and artificial intelligence (AI) take data science to an advanced level by enabling machines to learn from large, complex, and unstructured datasets. This step helps you understand how intelligent systems mimic human learning, recognize patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention.
- AI Fundamentals: Learn what artificial intelligence is and how it differs from machine learning and deep learning.
- Neural Networks Basics: Understand neurons, layers, activation functions, and how neural networks learn from data.
- Deep Learning Models: Study models like artificial neural networks (ANNs), convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and recurrent neural networks (RNNs).
- Common Use Cases: Explore applications such as image recognition, natural language processing, and recommendation systems.
- Popular Frameworks: Get familiar with TensorFlow and PyTorch for building and training deep learning models.
Learning deep learning and AI basics helps you understand how intelligent systems work, recognize complex patterns in data, and build smarter solutions for real-world problems using advanced models and tools.
Also Read: Data Analyst Salary in India (Freshers & Experienced)
Step 11: Work with Big Data and Cloud Platforms
As data grows in size and complexity, traditional tools are not always enough to handle it. Big Data and cloud platforms help you store, process, and analyze massive datasets efficiently. This step focuses on working with large-scale data and modern cloud-based environments used by companies.
- Big Data Basics: Learn what big data is and understand concepts like volume, velocity, and variety of data.
- Big Data Tools: Get familiar with tools such as Hadoop and Spark for distributed data processing.
- Cloud Platforms: Learn how platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure support data storage and analytics.
- Data Storage Solutions: Understand cloud storage options like data lakes, data warehouses, and object storage.
- Scalable Processing: Learn how cloud services help scale data processing and analysis efficiently.
Working with big data and cloud platforms enables you to manage large datasets smoothly and apply data science solutions in real-world, enterprise-level environments.
Step 12: Build Real-World Projects and a Data Science Portfolio
Building real-world projects helps you apply your data science skills to practical problems. By working on projects, you gain hands-on experience with data collection, cleaning, analysis, and model building. Projects also help you understand how different tools and techniques come together in real scenarios.
A strong data science portfolio showcases your skills to employers and recruiters. It highlights your problem-solving ability, coding skills, and understanding of data-driven solutions. Well-documented projects with clear explanations increase your credibility and improve your chances of landing data science roles.
Step 13: Learn Model Deployment and MLOps Basics
Model deployment and MLOps focus on making machine learning models usable in real-world applications. Trained models are deployed to production environments, where they work with live data and support business systems.
- Model Deployment Basics: Learn how to deploy models using APIs, web services, or cloud platforms.
- MLOps Concepts: Understand version control, experiment tracking, and managing model lifecycle.
- Model Monitoring: Learn how to track model performance, accuracy, and data drift over time.
- Automation Pipelines: Understand CI/CD pipelines to automate model training, testing, and deployment.
- Scalability and Reliability: Learn how to ensure models handle real-world traffic and scale smoothly.
Learning model deployment and MLOps helps you maintain reliable models in production and ensures your data science solutions deliver consistent value in real-world systems.
Step 14: Prepare for Data Science Jobs and Interviews
Preparing for data science jobs requires a strong understanding of core concepts, tools, and practical problem-solving skills. You should revise important topics such as statistics, Python, SQL, machine learning, and data visualization. Learning how to explain your projects clearly also plays a key role in interviews.
Regular practice of interview questions, case studies, and coding problems helps build confidence. Creating a strong resume, improving your portfolio, and preparing for both technical and HR interview rounds increase your chances of getting hired.
You can join our Data Science course (A Mentorship Program) by WsCube Tech. The program offers expert mentorship, real-world projects, interview preparation, and hands-on learning to help you start your career with confidence.
Following the complete data science roadmap helps you stay organized, build skills step by step, and move confidently toward job-ready expertise in data science.

Career Opportunities After Learning Data Science
Completing a structured data science roadmap opens doors to high-demand roles where data skills solve real-world problems and drive smarter decisions. Below are career opportunities you can explore after building strong data science skills.
- Data Scientist: Analyze large datasets, build predictive models, and generate insights using statistics, machine learning, and programming to support business strategy and data-driven decision-making.
- Data Analyst: Collect, clean, and analyze data to create reports and dashboards that help organizations understand trends, measure performance, and make informed operational decisions.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Design, build, and deploy machine learning models into production systems, focusing on scalability, performance, and real-world application of AI solutions.
- Business Intelligence Analyst: Transform raw data into meaningful dashboards and visual reports that help stakeholders track metrics, identify patterns, and improve business planning.
- AI Engineer: Develop intelligent systems using machine learning and deep learning techniques to automate processes, improve products, and build smart applications across industries.
Building strong skills and real-world experience helps you grow confidently in these roles and adapt to new opportunities as data science continues to evolve.
Data Scientist Demand and Salary (2026)
With businesses increasingly depending on data-driven decision-making, the demand for data science professionals is rising across industries. The global data science market, including data science platforms and data scientist roles, was valued at USD 95.31 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 27.6%, showing strong worldwide demand.
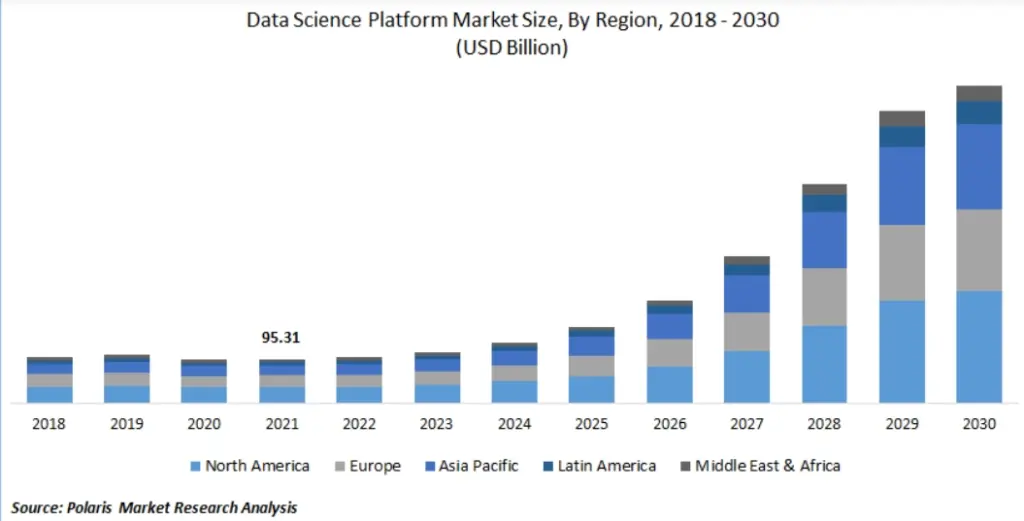
In India, companies are actively hiring data scientists who can analyze complex datasets, identify patterns, and deliver meaningful insights that influence business strategy and growth. Skills in statistics, mathematics, programming, and machine learning significantly improve job opportunities, salary prospects, and long-term career growth in the evolving tech landscape.
Data Scientist Salary in India
| Experience Level | Average Salary Range |
| Fresher (0–2 years) | ₹11.1 LPA – ₹12.3 LPA |
| Mid-Level (2–5 years) | ₹17.2 LPA – ₹19.1 LPA |
| Experienced (5+ years) | ₹17.2 LPA – ₹30+ LPA |
With growing data adoption, strong salary potential, and opportunities across startups, enterprises, and global companies, data science remains a future-proof and rewarding career choice in India for 2026 and beyond. Salary levels can vary depending on factors such as skills, location, company, industry, and overall experience.
Data Scientist Roadmap (Video Guide)

FAQs About Data Scientist Roadmap
Data science is the process of collecting, analyzing, and understanding data to find useful insights. You use statistics, programming, and machine learning to solve problems, predict outcomes, and support better decisions in real-world situations.
Yes, our data science roadmap is suitable for beginners if you start step by step. You begin with basics like data, statistics, and Python, then slowly move toward machine learning. A clear data science roadmap for beginners helps you learn without confusion.
You can learn basic data science skills in 6–8 months with consistent practice. To become job-ready, you may need 10–12 months, depending on your learning speed, background, and how closely you follow a structured data science career roadmap.
You do not need advanced math at the start. You mainly need basic statistics, probability, and linear algebra. You can learn these gradually while practicing. Over time, your confidence improves as you apply math concepts to real data problems.
You should start with Python because it is easy to learn and widely used in data science. Python libraries help you analyze data, create visualizations, and build machine learning models efficiently, making it ideal for beginners following a data scientist learning roadmap.
Yes, SQL is very important because most data is stored in databases. You use SQL to fetch, filter, and combine data before analysis. Strong SQL skills speed up and improve the accuracy of data handling in real-world data science projects.
You should build projects like data analysis dashboards, data cleaning tasks, prediction models, and simple machine learning applications. Working with real-world datasets helps you apply concepts, improve problem-solving skills, and strengthen your practical understanding of data science.
You do not need a specific degree to become a data scientist. Skills matter more than degrees. If you learn data science concepts, practice regularly, build real projects, and follow a clear data science roadmap, you can enter this field successfully.
Yes, data science is a good career in 2026 because companies across industries continue to rely on data for decision-making. There are strong opportunities in startups, enterprises, and global companies. By following the best data science roadmap, you can build in-demand skills, stay relevant, and remain job-ready in a competitive market.
You stay consistent by setting small goals, practicing daily, and building projects regularly. Following a clear road map for data science keeps you focused. Learning step by step helps you avoid overwhelm and make steady progress over time.
Read more blogs








Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Comments (0)
No comments yet.