Why do you pick one brand over another even if the price is higher? Why do some businesses become memorable while others feel forgettable?
The answer is simple—branding.
In this complete guide to branding in marketing, you’ll understand what branding means, why it shapes customer decisions, and how businesses use it to build trust, loyalty, and long-term growth.
As someone who has helped thousands of learners and businesses through WsCube Tech, we see every day how powerful branding can be when done right. Whether you’re a student, founder, marketer, or small business owner, this guide will show you exactly how branding works and how you can use it to build a standout identity.
What is Branding?
Branding is the process of creating a unique identity, personality, and perception for your business in the minds of customers. It’s not just your logo or your color palette; branding is every interaction people have with your business, from the way your website looks to how you talk on Instagram to how your customers feel when they use your product.
Branding shapes how people remember you. It builds an emotional connection. And it helps people trust your business even before they buy from you.
In simple words:
Branding is the story people tell about your business when you’re not in the room.
Importance of Brand in Marketing
Branding is not optional. It is one of the strongest growth levers for any business, large or small. This is the importance of branding in marketing:
Branding Builds Trust & Credibility
When your brand looks professional, communicates clearly, and stays consistent, people trust you without second thoughts. Trust directly increases sales.
It Helps Customers Recognize You Instantly
A strong brand is easy to spot anywhere—online or offline. This instant recognition makes people choose you faster.
Branding Creates Emotional Connection
People don’t buy products; they buy feelings. Strong branding makes your business relatable, memorable, and meaningful.
Gives You a Competitive Advantage
Even if your competitors offer the same product, a stronger brand wins more customers and more loyalty.
Recommended Professional Certificates
Digital Marketing Mentorship Program
Advanced AI Marketing Bootcamp
Performance Marketing Bootcamp
SEO Specialist Bootcamp
Helps You Charge Premium Prices
People pay more for brands they trust. Branding increases perceived value and allows you to set higher prices.
Creates Loyal, Repeat Customers
Strong branding keeps people coming back again and again. Loyalty reduces marketing costs and boosts long-term revenue.
Attracts Better Employees & Partners
A respected brand attracts skilled people, investors, and collaborators. People want to associate with trustworthy, well-known brands.
Helps You Expand Faster
Once your identity is strong, entering new markets, launching new products, or franchising becomes easier.
Key Components and Features of Branding
1. Brand Purpose
Brand purpose defines the deeper reason your business exists beyond profit. It answers the question, “Why are we doing this?”
A clear purpose inspires employees, attracts customers, and creates emotional connection. When people believe in your purpose, they trust your brand more.
Example: Nike’s purpose—“To bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete”, helps the brand stand for empowerment, not just sportswear.

2. Brand Vision
Brand vision expresses the long-term future your company aims to create. It guides strategic decisions, sets long-term direction, and keeps your team aligned with a shared dream. A strong vision motivates people and creates a sense of mission.
Example: Tesla’s vision—“To accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy”, drives their innovation, design, and business expansion.
3. Brand Mission
The mission explains what your business does daily to achieve its long-term vision. It focuses on practical actions, target audience, and the value you deliver. A clear mission helps customers understand your core offering quickly.
Example: Google’s mission—“To organize the world’s information”, captures their day-to-day purpose across search, maps, Gmail, and AI tools.
4. Brand Values
Values are the non-negotiable beliefs and principles that guide how your brand behaves. They influence hiring, culture, customer experience, and decision-making. Customers trust brands that stay true to their values consistently.
Example: Patagonia stands for environmental responsibility. Their values reflect in product materials, campaigns, and sustainability initiatives.
Also Read: The 5 D’s of Digital Marketing: Comprehensive Guide
5. Brand Story
Your brand story narrates who you are, why you started, the challenges you faced, and what motivates your mission. Stories make brands human, relatable, and memorable by creating emotional connection. A strong story keeps customers loyal even when competitors offer similar products.
Example: Mamaearth’s story of worried parents seeking toxin-free products helped build massive trust among new mothers.
6. Brand Personality
Brand personality refers to the human traits your brand expresses—friendly, luxurious, bold, playful, serious, or innovative. It influences how you speak, behave, and interact. A consistent personality helps customers easily connect with your brand.
Example: Fevicol’s personality is humorous and witty, while Apple’s is minimalist, premium, and sophisticated.
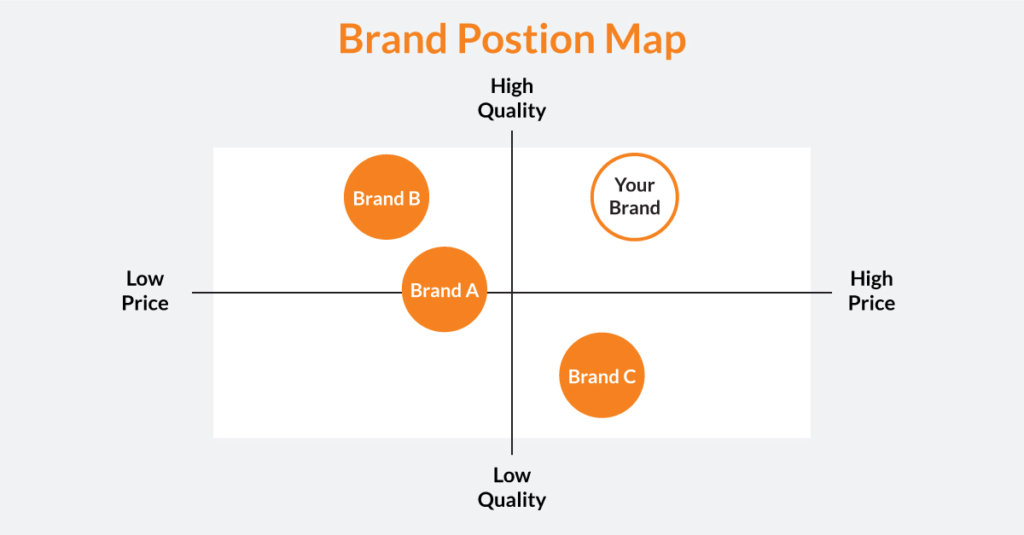
7. Brand Positioning
Positioning defines how you want customers to perceive you compared to competitors. It highlights your uniqueness and the benefit that makes you the preferred choice. A strong position helps customers choose without confusion.
Example: Volvo positions itself around “the safest cars,” creating an identity built on trust and reliability.
8. Brand Promise
Your brand promise is the commitment you make to customers about what they can expect every time they interact with your brand. It must be specific, believable, and consistently delivered through actions.
Example: FedEx promises overnight delivery. This commitment influences their service quality, operations, and communication.
9. Brand Voice
Brand voice represents the consistent style, language, and personality used in all communication. It shapes how your brand sounds to people—professional, casual, humorous, authoritative, or inspirational.
Example: Zomato’s voice is witty and fun, while IBM’s tone is formal, precise, and expert-driven.
10. Brand Messaging
Messaging includes your core message, tagline, slogan, and value proposition. It explains who you help, what you offer, and why it matters. Clear messaging helps customers understand your brand within seconds.
Example: L’Oréal’s message—“Because you’re worth it”, connects emotionally and positions the brand around self-confidence and empowerment.
Visual Identity: The Look & Feel of Your Brand
1. Logo
Your logo is the most recognizable symbol of your brand. It must be simple, timeless, and meaningful. A strong logo communicates your personality and helps people identify your brand instantly across packaging, website, and ads.
Example: Apple’s clean, minimal logo reflects innovation, simplicity, and premium quality.

2. Color Palette
Colors evoke emotions, influence buying decisions, and reinforce brand identity. A defined color palette ensures consistency across all platforms—website, packaging, marketing materials, and social media. Consistent colors help customers remember your brand faster.
Example: Coca-Cola’s red symbolizes energy and excitement; Facebook’s blue represents trust and reliability.
3. Typography
Typography conveys tone, personality, and professionalism. The fonts you choose—serif, sans-serif, script, or display—must align with your brand's identity and remain consistent in all communications. Good typography improves readability and strengthens brand recall.
Example: Google uses clean sans-serif fonts to communicate simplicity, clarity, and modernity.

4. Imagery Style
Your imagery style includes the type of photos, illustrations, graphics, and visual themes you use. A defined style—minimalistic, vibrant, emotional, or artistic—creates a cohesive experience wherever your brand appears.
Example: Airbnb uses warm, authentic images that highlight real people and real homes, promoting belonging and trust.
5. Iconography
Consistent icons improve user experience and strengthen brand identity across apps, websites, menus, and dashboards. Icons must match your overall design style—sharp, rounded, bold, thin, or minimalist.
Example: Uber’s simple black-and-white icon set supports its premium, no-nonsense brand identity.
6. Packaging Design
Packaging is often the first physical interaction customers have with your brand. Great packaging communicates quality, care, and personality while influencing purchase decisions. It should reflect your color palette, message, and values.
Example: Apple’s white, minimal packaging creates a premium unboxing experience aligned with its brand story.
7. Website UI/UX
Your website visually reflects your brand identity and shapes customer trust within seconds. Consistent colors, fonts, layout, and tone create a strong brand experience. A well-designed website improves conversions, engagement, and brand loyalty.
Example: Notion’s clean, calm UI reflects its purpose: productivity, clarity, and simplicity.
8. Brand Guidelines (Brand Book)
Brand guidelines define the exact rules for using your logo, colors, fonts, visuals, and tone. A brand book ensures every designer, employee, or partner maintains consistency across every touchpoint—ads, social media, packaging, and website.
Example: Companies like Google and Airbnb maintain detailed brand books to protect their identity.
Upcoming Masterclass
Attend our live classes led by experienced and desiccated instructors of Wscube Tech.
Types of Branding in Marketing
The types of branding include:
1. Corporate Branding
Corporate branding focuses on shaping the identity of the entire company, not just one product. It reflects the company’s philosophy, values, culture, and reputation. Strong corporate branding builds large-scale trust and influences customer expectations across all offerings.
Example: Tata is trusted across industries, including steel, automobiles, and hospitality, because the corporate brand stands for ethics, quality, and reliability.
2. Product Branding
Product branding gives each product its own identity, logo, features, and marketing style. This helps products stand out even within the same company and target different audiences effectively. Product branding works well in consumer goods and technology.
Example: Coca-Cola, Sprite, and Fanta all have different personalities, colors, and flavors while belonging to the same parent company.
3. Personal Branding
Personal branding highlights an individual’s identity, skills, personality, achievements, and influence. It helps people build trust, authority, and opportunities in careers, business, and social media. Strong personal brands attract followers, partnerships, and leadership roles.
Example: Virat Kohli, Gary Vaynerchuk, and Sandeep Maheshwari built powerful personal brands that influence millions.
4. Service Branding
Service branding focuses on delivering consistent experiences, quality, support, and reliability. Unlike products, services are intangible, so customers judge the brand based on their experience. A strong service brand wins through speed, trust, and seamless experience.
Example: Marriott hotels deliver premium hospitality globally, keeping service quality consistent across all locations.
5. Retail Branding
Retail branding shapes the identity of physical stores and shopping experiences. It includes store layout, ambience, staff behavior, product arrangement, and customer experience. Retail branding directly influences footfall and sales.
Example: Decathlon provides an interactive, open, and sports-focused environment across all stores to support exploration and engagement.
6. Digital Branding
Digital branding creates an identity through online platforms like websites, social media, apps, and digital ads. It focuses on visibility, engagement, tone, visuals, and storytelling online. Strong digital brands thrive on consistent content and personality.
Example: Zomato dominates with witty content and strong online presence, making its digital branding iconic.
7. Cultural Branding
Cultural branding uses societal values, traditions, festivals, and cultural stories to build emotional connection. It resonates deeply with local communities and drives loyalty through shared experiences.
Example: Amul’s iconic topical ads reflect Indian culture, humor, and festivals, keeping the brand relevant for decades.
8. Luxury Branding
Luxury branding revolves around exclusivity, sophistication, scarcity, premium craftsmanship, and aspirational value. Luxury brands rely on storytelling, superior design, and high perceived value to maintain a premium identity.
Example: Louis Vuitton and Gucci focus on heritage, craftsmanship, and exclusivity rather than mass-market appeal.
9. Rebranding
Rebranding involves updating a brand’s identity, visuals, messaging, or positioning to stay modern, relevant, or competitive. It helps brands refresh image, target new audiences, or correct previous weaknesses.
Example: Instagram’s shift from the brown camera icon to a vibrant gradient logo modernized the brand instantly.

Read More Marketing Guides
What is Brand Positioning?
Brand positioning is the unique space your brand occupies in the minds of customers. It defines how you want people to see your business compared to your competitors. Your positioning tells customers what makes you different, better, or more valuable. When done right, it helps people choose you instantly without comparing too much.
A strong brand positioning focuses on one core idea—quality, price, innovation, convenience, safety, luxury, or emotional value. You cannot be everything for everyone. Positioning makes your identity sharp.
Real Example:
How Volvo Positions Its Brand:
Volvo has positioned itself as the safest automobile brand in the world.
- Their ads highlight safety features, not luxury or speed.
- They engineer cars with world-class safety technology.
- They consistently communicate “safety first” in every message.
- They innovate features like side-impact airbags before others.
Because of this consistent positioning, customers who value safety choose Volvo without thinking twice. This is how powerful and clear positioning creates a strong perception and loyal customer base.
Must Read: 150+ Digital Marketing Terminologies (Terms & Glossary)
What is Brand Storytelling?
Brand storytelling is how you narrate the journey, purpose, values, and impact of your brand in a way that emotionally connects with people. Instead of listing product features, storytelling makes customers feel something. It humanizes your brand and builds long-term trust.
Good storytelling includes:
- A relatable beginning
- A struggle or real insight
- A mission or transformation
- A clear emotional message
Stories make people remember you, talk about you, and trust you.
Real Examples of Brand Storytelling
Nike – “Just Do It”
Nike rarely talks about shoes. They tell stories of athletes pushing limits, overcoming fear, and believing in themselves.
Nike’s storytelling focuses on courage and personal achievement. This emotional narrative makes customers feel inspired, not sold to.
The Branding Process
1. Research & Competitor Analysis: Study your market, audience, trends, and competitors.
2. Identify Your Target Audience: Define who you want to serve—age, location, interests, problems, aspirations.
3. Define Purpose, Vision, Mission & Values: These shape the foundation of your brand.
4. Create Your Brand Positioning Statement: This clarifies how you’re different from others.
5. Design Your Brand Personality & Voice: Choose how your brand behaves, speaks, and connects.
6. Build Your Visual Identity: Logo, colors, fonts, icons, and brand guidelines.
7. Craft Brand Messaging: Tagline, slogan, brand voice lines, and core communication.
8. Launch Your Brand: Website, social media, packaging, offline launch events.
9. Monitor Brand Reputation: Reviews, ratings, online mentions, social feedback.
10. Evolve & Optimize Your Brand Over Time: Brands grow, evolve, and adapt to market changes.
Branding Mistakes to Avoid
- Inconsistent Design & Messaging: Customers get confused and lose trust.
- No Clear Audience: Branding becomes directionless.
- Copying Competitors: You lose originality and identity.
- Poor Logo or Color Choices: This affects your brand’s credibility.
- Changing Identity Too Often: It breaks customer recognition.
- Weak Online Presence: People cannot trust what they cannot find.
- Not Monitoring Feedback: Ignoring reviews damages reputation.
Best Branding Examples
- Nike: Users feel empowered and motivated. Emotional storytelling is their superpower.
- Apple: Minimalism, premium design, and exclusivity define their identity.
- Zomato: Relatable content and witty tone make them a “people’s brand.”
- Fevicol: Memorable ads, humor, and creative storytelling.
- Coca-Cola: Branding built around happiness, sharing, and celebration.

FAQs About Branding
Branding is who you are, while marketing is how you promote yourself. Branding creates identity; marketing communicates that identity to the audience.
Brand identity is the visual and verbal representation of your brand—logo, colors, fonts, imagery, tone, and communication style.
Brand personality refers to human-like traits associated with your brand—fun, bold, premium, friendly, or professional.
Your brand story explains why you started, the emotion behind your journey, the problems you solve, and how you impact people’s lives.
Brand voice is the tone and style your brand uses while communicating. It stays consistent across social media, website, ads, and emails.
Brand equity represents the value your brand holds in the market. Strong equity means higher loyalty, pricing power, and customer preference.
Branding builds familiarity and trust. People buy from brands they recognize and feel connected to, resulting in higher conversions and repeat purchases.
When the brand becomes outdated, loses relevance, faces reputation issues, enters new markets, or needs to differentiate from competitors.
Digital branding is building your identity online through website, social media, content, SEO, email, and digital ads.
Through brand awareness, customer loyalty, engagement, search volume, repeat purchases, reviews, reputation, and brand recall.
Storytelling emotionally connects customers with your journey and values. It makes your brand memorable and human.
Any interaction a customer has with your brand—website, ads, packaging, support, social media, store visit, or email.
Yes. Strong branding helps small businesses gain trust, compete with bigger brands, attract customers, and grow consistently.
Emotional branding focuses on connecting with customers’ feelings rather than just rational benefits. It builds deep loyalty.
Co-branding is when two brands collaborate to create a product or campaign, combining their strengths.
Explore Our Free Courses








Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Comments (0)
No comments yet.