In software development, an SDE (Software Development Engineer) builds, improves, and maintains applications used in real life. This role needs strong problem-solving skills, solid coding basics, and a clear understanding of how different software components work together. Without proper direction, learning can feel confusing and unstructured, especially for beginners who are unsure where to begin.
This Software Development Engineer roadmap offers a clear and structured learning path, guiding you from basic concepts to advanced skills. It helps you understand what to learn first, how different topics connect, and how to practice effectively. By following this roadmap, you can build strong fundamentals, avoid common mistakes, and prepare with confidence for interviews and long-term career growth.
Who is a Software Developer Engineer?
A software developer is a professional who designs, builds, tests, and maintains software applications. They write code to solve problems, create features, and improve systems used on computers, mobile devices, and the web. Software developers also debug issues, update applications, and work with teams to turn ideas into reliable, user-friendly software solutions.
Role and Responsibilities of a Software Developer
Software developers build and maintain applications that solve real-world problems. They convert ideas into working software using code, logic, and collaboration. Below is the list of key responsibilities of a software developer to help you understand the role better.
- Write clean, efficient, and reusable code that meets user and business requirements while following best coding practices.
- Identify, debug, and fix errors to improve application stability, performance, and reliability.
- Collaborate with designers, testers, and other developers to plan, build, and deliver software features.
- Test applications regularly to ensure quality, security, and a smooth user experience across platforms.
- Maintain and update software by adding new features, improving functionality, and responding to user feedback.
SDE Roadmap 2026: Step-by-Step Learning Guide
This guide provides a clear path to becoming a Software Development Engineer. Following our software engineer roadmap for beginners helps you learn in the right order, build strong fundamentals, and move confidently toward real-world development and technical interviews. Below are the key steps you should follow to build strong fundamentals and grow in your SDE journey:
- Learn One Programming Language Well
- Build a Strong Foundation in Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA)
- Master Core Computer Science Subjects
- Computer Networks
- Database Management Systems (DBMS)
- Operating Systems
- Computer Architecture
- Software Engineering Basics
- Learn Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Concepts
- Learn High-Level Design (HLD) and Low-Level Design (LLD) for Interviews
- Build Hands-On Projects
- Get Certifications in Trending Technologies
- Sharpen Soft Skills and Analytical Skills
- Prepare for Interviews by Solving Practice Questions
- Understand Question Patterns for SDE-1, SDE-2, and SDE-3 Roles
Next, we will go through each step one by one to clearly explain what you should learn, how to practice effectively, and how to progress confidently in your SDE learning journey.
Recommended Professional Certificates
Full Stack Development Mentorship Program
WordPress Bootcamp
Step 1: Learn One Programming Language Well
Begin by choosing one programming language and focus on understanding its fundamentals clearly. Start with syntax, variables, conditions, loops, functions, and basic logic. Once you are comfortable with these basics, gradually move on to advanced features of the language.
You can choose languages such as C, C++, Java, Python, or others. In the early stage, languages like C, C++, or Java are often preferred because they help you understand memory management, program execution, and performance at a deeper level.
Learning a language is not only about writing code. Over time, you should understand how the language works internally, how it manages memory, and which operations are efficient. Focus on coding first, and later explore deeper concepts using free resources by WsCube, where you can learn programming from basics to advanced levels.
Step 2: Build a Strong Foundation in Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA)
Once you are comfortable with your chosen programming language, the next step is to learn data structures and algorithms. DSA helps you write efficient code and solve problems in an optimized way. It is a key focus area for product-based companies and technical interviews.
Data Structures
Learn commonly used data structures such as arrays, stacks, queues, linked lists, sets, hash maps, trees, graphs, and heaps. Understand why each structure is used, where it fits best, and practice using them in real code. Try to implement them yourself to understand their working.
Algorithms
Start with basic searching and sorting algorithms like linear search, binary search, bubble sort, insertion sort, merge sort, and quick sort. After that, move to advanced topics such as recursion, backtracking, dynamic programming, greedy algorithms, and graph-based algorithms.
Step 3: Master Core Computer Science Subjects
Core computer science subjects help you understand how software works internally, including program execution, data management, and system behavior. Below, we will discuss the core computer science concepts that are important for building strong fundamentals, writing better code, and performing well in real-world projects and technical interviews.
3.1 Computer Networks
Computer Networks explain how computers and devices communicate with each other over the internet or local networks. They cover how data is sent, received, and routed between systems, helping you understand concepts like requests, responses, and network communication.
For an SDE, computer networks are used when building web applications, APIs, and distributed systems. They help you understand how client–server communication works, how data flows between services, and how applications handle network delays, security, and scalability in real-world software systems.
3.2 Database Management Systems (DBMS)
Database Management Systems focus on how data is stored, organized, and managed in software applications. DBMS helps you understand data models, relationships, queries, and transactions, making data reliable, secure, and easy to retrieve.
For SDE-1, you should learn SQL basics, CRUD operations, joins, indexes, and normalization. For SDE-2 and SDE-3, the focus shifts to advanced querying, performance optimization, transactions, concurrency control, scalability, replication, and designing databases for large and distributed workloads.
3.3 Operating Systems
Operating Systems explain how a computer manages both hardware and software resources. They control how programs are executed, how memory is allocated and released, how files are stored, and how multiple tasks run at the same time, allowing applications to function smoothly.
A good understanding of operating systems helps you write more efficient and reliable programs. It teaches you how processes and threads work, how memory is managed, and how the system handles multitasking. This knowledge also helps in debugging performance issues, handling resource limits, and understanding how applications behave under different system loads.
3.4 Computer Architecture
Computer Architecture explains how a computer system is structured and how hardware components like the CPU, memory, and input/output devices work together to execute programs.
Computer architecture is considered an advanced topic and is mainly relevant for SDE-2 and SDE-3 roles. It helps in understanding system performance, low-level behavior, and how software decisions impact hardware efficiency.
3.5 Software Engineering Basics
Software engineering basics focus on how software is planned, developed, tested, and maintained in a structured way. This topic helps you understand the full software development lifecycle, from requirements to deployment.
It includes practices like clean coding, documentation, version control, and testing. These practices help improve code quality and teamwork.
Understanding software engineering basics helps you work effectively in real projects. It improves collaboration, code management, and the ability to deliver reliable software that meets user and business needs.
Step 4: Learn Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Concepts
Object-Oriented Programming is an important concept in software development that helps you write clean, structured, and reusable code. Languages like C++, Java, and C support OOP concepts, making them widely used in real-world applications and enterprise systems.
OOP helps you break large problems into smaller parts using classes and objects. This makes code easier to understand, maintain, and extend. Strong OOP knowledge is useful for building scalable applications and is commonly tested in SDE interviews.
Features of OOP
- Encapsulation: Groups data and methods together, improving security and code organization.
- Inheritance: Allows one class to reuse properties and methods of another, reducing code duplication.
- Polymorphism: Enables one function or method to behave differently based on usage or input.
- Abstraction: Hides complex implementation details and shows only essential features to the user.
Upcoming Masterclass
Attend our live classes led by experienced and desiccated instructors of Wscube Tech.
Step 5: Learn High-Level Design (HLD) and Low-Level Design (LLD) for Interviews
High-Level Design and Low-Level Design help you understand how software systems are planned and built. HLD focuses on the overall structure of a system, while LLD focuses on detailed class and code-level design. Learning both improves your ability to design clear and maintainable systems.
For SDE-2 and SDE-3 roles, there is usually a System Design interview round. In this round, you are asked to design real-world systems, explain your approach, and discuss scalability and performance. Strong HLD and LLD knowledge is important to succeed in these interviews.
LLD Roadmap
- Object-Oriented Design Principles
- Classes and Relationships (UML Basics)
- Design Patterns (Singleton, Factory, Observer, etc.)
- SOLID Principles
- Low-Level Design of Real Problems (Parking System, BookMyShow, etc.)
HLD Roadmap
- System Requirements and Use Cases
- High-Level Architecture and Components
- Scalability and Load Handling
- Database Design and Data Flow
- Caching, Messaging, and API Design
This structured approach helps you prepare effectively for system design interviews and real-world software architecture discussions.
Step 6: Build Hands-On Projects
Building hands-on projects helps you understand how software works in real situations. These projects show how different concepts come together and also help you build a strong GitHub portfolio for SDE interviews.
Below are some important projects, explained clearly, along with GitHub reference links you can explore or use for guidance.
- Student Management System: This project helps you learn CRUD operations, database integration, and basic backend logic. You can manage students, courses, and records using forms and APIs.
- To-Do / Task Management Application: This project focuses on application flow, user input handling, and data storage. You learn how to add, update, delete, and track tasks efficiently.
- Online Bookstore / E-commerce Application: This project teaches user authentication, product listings, cart management, and order processing. It helps you understand real-world business logic and backend workflows.
- REST API Development Project: Building REST APIs helps you understand client–server communication, request handling, status codes, and data exchange. This project is very important for backend SDE roles.
- Blog or Content Management System (CMS): This project helps you work with user authentication, database relationships, and content handling. You learn how to manage posts, users, and permissions.
These projects help you apply theory to practice, improve problem-solving skills, and showcase your work on GitHub. Always try to build projects from scratch first, then compare them with GitHub repositories to learn better design and coding practices.

Step 7: Get Certifications in Trending Technologies
Professional certifications support personal growth and help you learn new skills that are used in companies. They allow flexible learning from anywhere, making them useful for students and working professionals. Certification courses help you upskill, specialize in one area, and improve your overall understanding of modern technologies.
Certifications also help you stay competitive in the job market. Structured courses follow the right learning flow and focus on best practices used in the industry. You can explore our website for certification courses that help you learn effectively and prepare with confidence.
Some of the popular certifications you can rely on are:
- IBM DevOps and Software Engineering Professional Certificate: Suitable for beginners, this certification covers software development basics along with DevOps tools, workflows, and modern development practices.
- AWS Certified Developer – Associate: Focuses on building, deploying, and debugging cloud-based applications using AWS services, which is important for developers working with scalable systems.
- Microsoft Azure Fundamentals: Introduces cloud concepts along with Azure services related to storage, development, networking, and security, making it useful for cloud-aware software engineers.
- Google Cloud Associate Cloud Engineer: Covers application deployment, cloud resource management, and monitoring, helping learners understand how cloud-based systems operate.
- Oracle SQL Certification: Strengthens database and SQL skills, including queries, joins, and data handling, which are essential for most software development roles.
As an engineer, you will keep learning new tools and technologies throughout your career. Certifications help you upskill regularly, build confidence, and show recruiters that you are ready for evolving industry needs.
Step 8: Sharpen Soft Skills and Analytical Skills
Soft skills and analytical skills are just as important as technical knowledge for a Software Development Engineer. They help you communicate ideas clearly, work well in teams, and solve problems effectively.
Good communication helps you explain your code, discuss solutions, and collaborate with teammates. Analytical skills improve your ability to think logically, break problems into smaller parts, and choose the best solution. Strong soft skills also help during interviews, team discussions, and career growth in the long run.
Step 9: Prepare for Interviews by Solving Practice Questions
Regular practice builds confidence, improves problem-solving speed, and helps you understand common interview question patterns. Consistent problem-solving prepares you for coding rounds, technical discussions, and behavioral interviews.
- Practice coding problems daily on basics like arrays, strings, and recursion to strengthen logic and build consistency.
- Gradually move to advanced topics such as trees, graphs, and dynamic programming to handle complex interview questions.
- Focus on writing clean, readable, and optimized code instead of just getting the correct answer.
- Revise core concepts regularly while practicing to keep fundamentals strong and avoid confusion during interviews.
- Analyze your mistakes carefully and work on weak areas to improve accuracy and confidence.
- Practice mock interviews to get comfortable with real interview pressure and time limits.
- Learn to explain your approach clearly, as interviewers value your thinking process along with the solution.
Step 10: Understand Question Patterns for SDE-1, SDE-2, and SDE-3 Roles
Different SDE levels focus on different skills and responsibilities. Understanding the question patterns for each role helps you prepare in the right direction and focus on what interviewers actually expect at that level.
SDE-1 (Entry-Level)
- Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA): Questions focus on arrays, strings, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, and basic graphs. You are expected to write correct and optimized solutions with clear logic.
- Problem Solving and Coding Skills: Interviewers check how you approach problems, handle edge cases, and write clean, readable code using one programming language confidently.
- Basic Object-Oriented Programming: You should understand classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, and how to apply OOP concepts in simple real-world scenarios.
- Core CS Fundamentals: Basic knowledge of DBMS, operating systems, and computer networks is tested to see if you understand how software works at a fundamental level.
SDE-2 (Mid-Level)
- Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms: Problems involve complex trees, graphs, dynamic programming, and optimization techniques. You are expected to write efficient solutions and justify time and space complexity.
- System Design (Basics to Intermediate): You may be asked to design small to medium-scale systems, focusing on scalability, APIs, databases, caching, and basic architecture decisions.
- Code Quality and Design Patterns: Interviewers evaluate how well you structure code, follow best practices, and use design patterns to build maintainable and reusable components.
- Project and Experience-Based Questions: You are asked about real projects, challenges faced, decisions made, and how you improved performance or fixed production issues.
SDE-3 (Senior-Level)
- System Design (HLD and LLD): The major focus is on designing large-scale systems, explaining the architecture, handling high traffic, and managing data flow across services.
- Scalability and Performance: Questions test how systems behave under load, how to reduce latency, and how to handle failures effectively.
- Leadership and Decision-Making: You may be asked about design choices, mentoring juniors, and making technical decisions in complex scenarios.
- Deep Technical Knowledge: Interviewers expect a strong understanding of core computer science concepts and real-world experience in building and maintaining systems.
Now that we have discussed all the steps, you can follow this software engineer roadmap to learn in the right order, build strong fundamentals, practice effectively, and prepare confidently for real-world development and SDE interviews.
Explore More Career Roadmaps
| SEO Roadmap | Digital Marketer Roadmap |
| Ethical Hacker Roadmap | Python Developer Roadmap |
| Data Analyst Roadmap | Data Scientist Roadmap |
| Mobile App Developer | WordPress Developer Roadmap |
Career Opportunities for SDEs
Software Development Engineers can grow into many roles based on their skills, experience, and interests. Below are the major career options explained clearly:
- Software Development Engineer (SDE): Works on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software systems. SDEs solve real-world problems using code and are involved in the complete development lifecycle.
- Backend Developer: Focuses on server-side development, APIs, databases, and business logic. Backend developers ensure applications are fast, secure, and scalable.
- Frontend Developer: Builds user interfaces and works on the visual part of applications. This role focuses on user experience, responsiveness, and performance of web or mobile apps.
- Full Stack Developer: Handles both frontend and backend development. Full stack developers understand complete application flow and are valuable in startups and product-based companies.
- System Design / Software Architect: Designs large-scale systems and defines how components interact. This role focuses on architecture, scalability, and long-term system planning.
- Technical Lead / Engineering Manager: Leads development teams, reviews code, makes technical decisions, and guides engineers. This role combines technical expertise with leadership responsibilities.
SDE Salary in India: Experience-Wise Breakdown
- Entry-Level (0–2 years): ₹11.8 LPA – ₹13 LPA
- Mid-Level (3–5 years): ₹15.7 LPA – ₹17.4 LPA
- Senior-Level (6+ years): ₹14 LPA – ₹20.8+ LPA
Salaries vary based on skills, company type, location, and interview performance. Product-based companies and strong system design skills often offer higher packages.
Real-World Applications of SDE Skills
Software Development Engineer skills are used daily to build, improve, and maintain technology-driven solutions.
1. Web Application Development
Software Development Engineers build fast, secure, and scalable web applications. They work on frontend, backend, and databases to deliver smooth user experiences for websites, dashboards, and online services.
2. Mobile Application Development
SDE skills are used to build Android and iOS applications used by millions of users. Engineers focus on performance, user-friendly interfaces, secure data handling, API integration, device compatibility, and smooth app behavior to deliver reliable and engaging mobile experiences.
3. Embedded Systems
In embedded systems, SDEs write software that runs on hardware devices like IoT products, automobiles, and smart appliances, focusing on efficiency, low memory usage, and real-time performance.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
SDEs integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning models into software applications to enable features such as recommendations, predictions, automation, and intelligent decision-making. They ensure models run efficiently, scale well, and work reliably within real-world production systems.
5. Cloud-Based Systems
SDE skills are used to build cloud applications that run on platforms like AWS, Azure, or GCP, focusing on scalability, availability, and cost-efficient resource usage.
Future Scope of Software Development Engineering
The future scope of Software Development Engineering is very strong and continues to grow. As technology evolves, SDEs will play a key role in building applications for cloud computing, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, IoT, and automation.
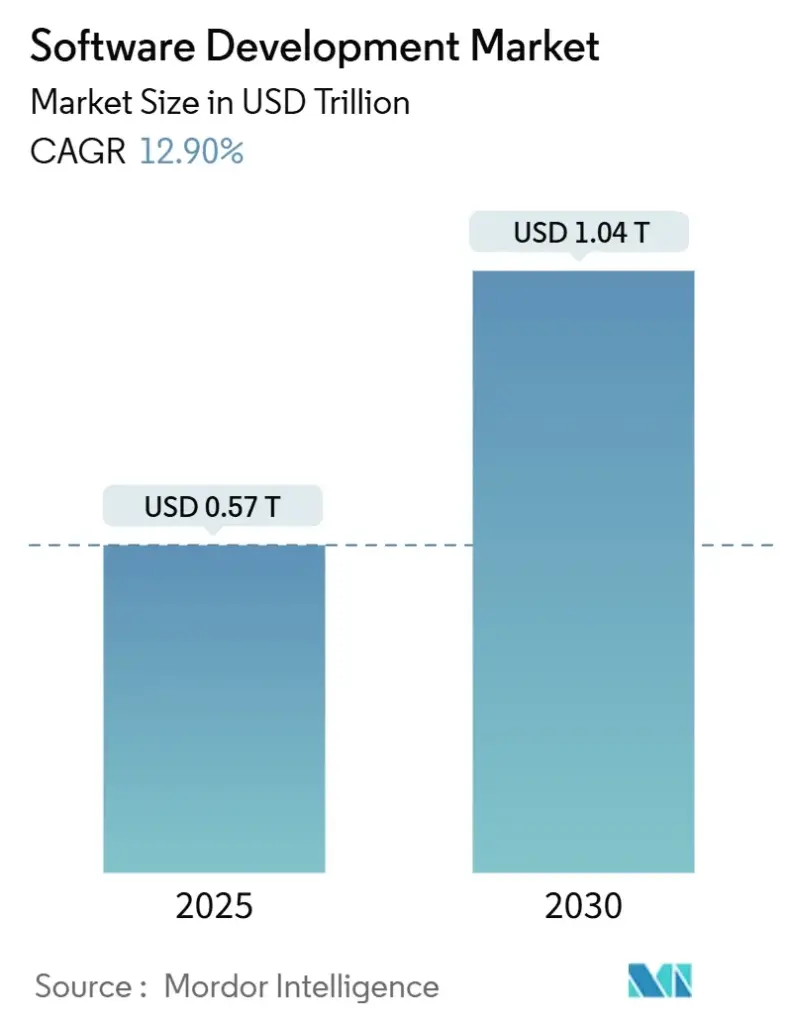
Image Source: Mordor Intelligence
With the rise of startups, product-based companies, and digital transformation, demand for skilled SDEs will remain high. Engineers who keep learning new technologies, improve system design skills, and adapt to industry trends will have long-term career growth, global opportunities, and leadership roles in the software industry.
SDE Learning Roadmap: Video Guide

FAQs About SDE Roadmap
A software engineer designs, builds, tests, and maintains software applications. You write code, solve problems, improve system performance, fix bugs, and collaborate with teams to create reliable and scalable software solutions.
You should follow an SDE roadmap if you are a beginner, student, or working professional who wants a clear direction to learn software development skills and prepare confidently for software engineering roles.
Yes, an sde roadmap for beginners helps you avoid confusion by showing what to learn first and what to learn next. It helps you build strong basics before moving to advanced topics.
You can become an entry-level SDE in about 8–12 months with regular practice and focused learning. The exact time depends on your background, learning pace, daily study time, and how consistently you work on coding, DSA, and projects.
You should start with one language like Python, Java, or C++. Choose a language that supports strong DSA practice and real-world development so you can use it throughout your software engineer roadmap.
No, you do not need a CS degree to become an SDE. With the right skills, projects, and preparation using a structured roadmap, you can crack interviews and build a strong software career.
DSA plays a key role because it improves problem-solving skills and is heavily tested in interviews. You need strong DSA knowledge to clear coding rounds and perform well as an SDE.
Yes, projects are very important because they help you apply concepts, understand real-world development, and strengthen your resume. Interviewers often judge your skills based on project experience.
An SDE roadmap helps you prepare systematically for interviews by covering DSA, core CS subjects, system design, and mock practice. It improves your confidence and helps you answer questions clearly.
The future of software engineers in 2026 looks very promising. You will find strong demand across industries, especially in cloud computing, AI, cybersecurity, and scalable systems, with companies valuing engineers who continuously upgrade skills and adapt to new technologies.
Free Courses for You







Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Comments (0)
No comments yet.