Generative AI is an advanced technology that creates new content such as text, images, audio, code, and videos using intelligent models. It learns from large datasets, understands patterns, and produces human-like outputs used in chatbots, content creation tools, image generators, and other real-world applications. These systems help automate tasks, improve creativity, and support faster decision-making across industries.
This generative AI roadmap provides a clear and structured learning path for beginners and professionals. It explains what to learn first, how to build strong basics, and how to move step by step toward advanced concepts. By following this roadmap, you can avoid confusion, focus on practical skills, and prepare confidently for real-world generative AI roles.
How Generative AI Works
Generative AI works by learning patterns from huge amounts of data and then using those patterns to create new content. Instead of just remembering information, the system understands how things connect, like how words form sentences, how sounds form speech, or how colors and shapes form images. When a user gives an input, called a prompt, the model predicts what should come next based on what it learned during training.
Working of Generative AI
- Data Collection: The model is trained using large datasets such as text, images, audio, or code.
- Model Training: Neural networks learn by making predictions and correcting mistakes over many cycles.
- Pattern Learning: The system understands structure, context, and relationships in the data.
- User Prompt: A user provides instructions or a question to guide the model.
- Content Generation: The model creates new text, images, music, or other outputs based on learned patterns.
- Model Improvement: Performance improves through fine-tuning, feedback, and better training data.
Why Learn Generative AI in 2026?
Generative AI is becoming one of the most important technologies of this decade. From chatbots and virtual assistants to AI-generated designs, videos, and code, companies across industries are adopting generative tools to improve productivity and reduce costs. Learning this technology now gives you an early advantage in a rapidly growing job market where demand for AI skills is rising every year.
In 2026, businesses are not just experimenting with AI, they are building real products around it. Startups and large companies alike need professionals who understand large language models, prompt engineering, and AI application development. By learning generative AI, you open doors to careers in AI engineering, research, automation, content creation, and intelligent app development.
Key Reasons to Learn Generative AI
- High Career Demand: Companies are actively hiring Generative AI engineers and AI developers.
- Future-Proof Skill: AI skills will stay relevant as automation continues to grow.
- Wide Industry Use: Used in healthcare, education, marketing, gaming, finance, and more.
- Freelance & Startup Opportunities: You can build AI tools, SaaS products, or offer AI services.
- Innovation Potential: Generative AI enables you to create products that were impossible before.
Recommended Professional Certificates
Full Stack Development Mentorship Program
WordPress Bootcamp
Generative AI Roadmap 2026: Step-by-Step
This generative AI roadmap explains a clear learning path to master skills, tools, and concepts required to build modern AI systems and grow as a professional generative AI engineer. Below are the steps to follow that will help you to become a skilled Gen AI engineer.
- Learn Python Programming Basics
- Master Python for AI
- Understand Mathematics for AI
- Learn Machine Learning Fundamentals
- Dive into Deep Learning
- Understand Natural Language Processing (NLP) Basics
- Learn Transformer Architecture
- Work with Large Language Models (LLMs)
- Prompt Engineering
- Fine-Tuning Generative Models
- Working with Diffusion Models
- Generative AI for Images, Audio, and Video
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- AI Agents and Tool Use
- Deployment of Generative AI Applications
- MLOps for Generative AI
- AI Safety and Responsible AI
- Performance Optimization
- Real-World Generative AI Projects
- Building a Generative AI Portfolio
Now, each step will be discussed in detail to help you learn concepts clearly, build practical skills, and apply generative AI confidently in real-world projects.
Step 1: Learn Programming Basics
Before diving into Generative AI, you need a strong foundation in programming. Programming helps you understand how to give instructions to a computer, use logical thinking, and develop problem-solving skills. It forms the base for everything you will do later, from training AI models to building real-world applications.
Start with basic Python concepts like variables, data types, loops, and conditional statements. Learn how functions work and how to break big problems into smaller steps. Focus on writing clean and simple code. Once you are comfortable with these basics, it becomes much easier to understand machine learning, deep learning, and AI development in the later stages of your journey.
Step 2: Master Python for AI
After learning basic programming, the next step is to use Python specifically for AI tasks. Python is powerful because of its rich ecosystem of libraries that make data handling, analysis, and model building much easier. Mastering these tools helps you move from simple coding to real AI development and prepares you to work with real-world AI datasets and workflows.
In AI projects, most of your time is spent preparing and understanding data before model training. Python makes this process efficient and structured. Learning how to explore datasets, handle missing values, and transform raw data into usable formats is a key skill at this stage. Below are the key concepts to learn:
- NumPy: Perform numerical and matrix operations that power AI and machine learning algorithms.
- Pandas: Load, clean, filter, and manipulate structured datasets efficiently.
- Matplotlib / Seaborn: Visualize data to understand patterns, trends, and relationships.
- File Handling: Work with CSV, JSON, Excel, and text datasets used in real AI projects.
- Virtual Environments: Manage project dependencies and maintain clean development setups.
Strong Python skills make it easier to preprocess data, support model training, and build Generative AI applications confidently in later steps.
Step 3: Understand Mathematics for AI
Mathematics explains how AI models work internally. You do not need deep math expertise, but understanding core concepts helps you grasp learning, prediction, and optimization. Focus on building intuition rather than memorizing formulas. Below are the key areas to focus on when learning the mathematics required for AI.
- Linear Algebra: Vectors, matrices, and matrix operations used in neural networks and embeddings.
- Probability: Understanding uncertainty, likelihood, and how models make predictions.
- Statistics: Mean, variance, distributions, and data interpretation.
- Calculus (Basics): Gradients and derivatives used in model training and optimization.
A basic understanding of these math concepts will make machine learning and deep learning much easier to learn in the next steps of your Generative AI journey.
Upcoming Masterclass
Attend our live classes led by experienced and desiccated instructors of Wscube Tech.
Step 4: Learn Machine Learning Fundamentals
Machine Learning (ML) is the core technology that allows systems to learn from data instead of being explicitly programmed. It helps computers find patterns, make decisions, and improve performance through experience. Understanding ML fundamentals is important because generative AI models are built on the same learning principles.
Here, focus on how data is used to train models and how predictions are generated. Learn the main types of machine learning and understand how models are tested, evaluated, and improved over time. Below are the key concepts to learn:
- Supervised Learning: Models learn from labeled data to make predictions.
- Unsupervised Learning: Systems detect patterns and relationships in unlabeled data.
- Training vs Testing Data: Splitting data to evaluate model performance.
- Model Evaluation: Accuracy, precision, recall, and other performance metrics.
- Overfitting & Underfitting: Understanding when a model learns too much or too little.
These machine learning fundamentals help you build strong data-driven thinking, understand model behavior, and create reliable AI systems that perform well on real-world datasets.
Step 5: Dive into Deep Learning
Deep learning is a branch of machine learning that uses multi-layer neural networks to identify complex patterns in large datasets. It powers modern generative AI systems like language models and image generators, enabling automatic feature learning from data and making it essential for building advanced intelligent applications. Below are the key concepts to focus on.
- Neural Networks: Understand neurons, layers, weights, and how information flows through a network.
- Activation Functions: Learn how functions like ReLU and Sigmoid help models learn non-linear patterns.
- Loss Functions: Understand how models measure errors during training.
- Backpropagation: Learn how models update weights to reduce errors.
- Popular Frameworks: Get started with TensorFlow or PyTorch for building deep learning models.
Learning deep learning fundamentals prepares you to work with advanced generative models in the next stages of your Generative AI roadmap.
Step 6: Understand Natural Language Processing (NLP) Basics
After deep learning, the next key area to explore is Natural Language Processing (NLP), which deals with how computers interpret and handle human language. NLP plays a major role in generative AI applications like chatbots, virtual assistants, translation systems, and text generation tools. Learning NLP basics helps you understand how textual data is cleaned, structured, and prepared before being used in language models.
- Text Preprocessing: Cleaning text by removing punctuation, stopwords, and unnecessary symbols.
- Tokenization: Breaking text into words, subwords, or sentences for model processing.
- Word Embeddings: Converting words into numerical vectors using methods like Word2Vec or GloVe.
- Part-of-Speech Tagging: Identifying grammatical roles such as nouns, verbs, and adjectives.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Detecting names of people, places, dates, and organizations in text.
Understanding NLP basics helps you build and work with language-based generative AI applications effectively.
Step 7: Learn Transformer Architecture
Transformer architecture is the backbone of modern generative AI models, including large language models and advanced text generation systems. It helps models understand context, meaning, and long-range relationships in text more effectively than traditional neural networks. Transformers power popular models such as GPT, BERT, and T5 and are essential for building high-performance generative AI applications. Below are the key concepts to learn:
- Self-Attention: Allows models to identify which words are most important in a sentence.
- Multi-Head Attention: Captures multiple relationships in text at the same time.
- Encoder–Decoder Structure: Manages how input text is processed and output text is generated.
- Positional Encoding: Preserves word order information in transformer models.
- Popular Transformer Models: Understand architectures like BERT, GPT, and T5.
Learning transformer architecture helps you work confidently with modern language models and advanced generative AI systems.
Explore More Career Roadmaps
Step 8: Work with Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large Language Models (LLMs) are the foundation of modern generative AI systems. They are trained on massive text datasets to understand language structure and context. Well-known models such as GPT, BERT, and T5 are widely used for tasks like text generation, summarization, translation, and question answering.
Working with LLMs helps you apply your learning to real-world scenarios. You learn how to use pre-trained models, design effective prompts, control outputs using parameters, and integrate models into applications such as chatbots, virtual assistants, search tools, and content generation platforms.
Step 9: Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering is the process of writing clear and structured instructions that guide generative AI models to produce accurate, relevant, and useful outputs. Well-designed prompts help models understand context and the expected response format.
Types of Prompts
- Zero-Shot Prompts: Ask the model to perform a task without providing examples.
- Few-shot Prompting: Providing multiple examples to help the model better understand the expected output style and format.
- Instruction-Based Prompts: Clearly state what the model should do using direct instructions.
- Role-Based Prompts: Assign a role to the model, such as an expert, teacher, or assistant.
- Multi-Step Prompts: Break complex tasks into smaller steps for better clarity.
Techniques for Better Responses
- Write clear and specific instructions
- Add relevant context to the prompt
- Define the expected output format
- Use examples when needed
- Apply constraints to control responses
- Refine and iterate prompts for better results
Prompt engineering skills help you communicate effectively with generative AI models and achieve consistent, high-quality results across different tasks and applications.
Step 10: Fine-Tuning Generative Models
Fine-tuning is the process of customizing a pre-trained generative model to perform better on specific tasks or domains using a smaller, targeted dataset. This approach improves accuracy, relevance, and efficiency without training a model from the beginning, making it practical for real-world AI applications.
- Transfer Learning: Reuse an already trained model and update its knowledge for a new task or application, saving time and resources.
- Domain-Specific Training: Uses specialized industry or topic-based data to improve the model’s understanding and output relevance in targeted applications.
- Fine-Tuning Methods: Apply full fine-tuning or parameter-efficient techniques such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to reduce computation cost and memory usage.
- Overfitting Control: Prevent the model from learning noise instead of useful patterns so it performs well on new, unseen data.
- Post-Training Evaluation: Test model performance using validation data to ensure reliability, accuracy, and real-world effectiveness.
Fine-tuning enables the creation of high-quality generative AI solutions such as specialized chatbots, content generators, and intelligent assistants.
Step 11: Working with Diffusion Models
Diffusion models are a powerful class of generative models used to create high-quality images, audio, and other media. They work by gradually adding noise to data and then learning how to reverse this process to generate new content. This technique enables highly detailed and realistic outputs, making diffusion models a core technology behind modern text-to-image and multimedia generation systems. Below are the key concepts to learn:
- Noise and Denoising Process: Understand how noise is added step by step and then removed to generate new samples.
- Latent Space Representation: Learn how images and other data are compressed into efficient representations for faster generation.
- Text-to-Image Generation: Explore how text prompts guide diffusion models to produce relevant and meaningful visuals.
- Sampling Techniques: Study different methods used to generate final outputs from learned data distributions.
- Popular Frameworks: Get familiar with libraries and tools commonly used to build and run diffusion models.
Learning diffusion models helps you build applications such as AI image generators, creative design tools, and multimedia content systems.
Step 12: Generative AI for Images, Audio, and Video
Generative AI is not limited to text. It also enables machines to create realistic images, natural-sounding audio, and dynamic videos using learned patterns from large multimedia datasets. This step helps you understand how generative models work across different data formats and how they are applied in creative and practical use cases such as design, media, entertainment, and content creation.
- Image Generation: Create images using models like diffusion models and GANs for art, design, and visual content creation.
- Audio Generation: Generate speech, music, and sound effects using models for text-to-speech and audio synthesis.
- Video Generation: Learn how AI creates or edits videos by generating frames, animations, or visual sequences.
- Multimodal Models: Understand models that combine text, image, and audio inputs for richer AI applications.
- Real-World Applications: Explore use cases in marketing, gaming, film production, education, and digital media.
Learning generative AI for images, audio, and video expands your ability to build creative, multi-format AI solutions beyond text-based systems.
Step 13: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) improves generative AI by combining language models with external knowledge sources. Instead of relying only on trained data, the model retrieves relevant information from documents or databases before generating responses. This approach increases accuracy, reduces hallucinations, and enables up-to-date, context-aware outputs for real-world applications.
- Document Retrieval: Fetch relevant text from PDFs, databases, or knowledge bases using search or embeddings.
- Vector Databases: Store and search document embeddings using tools like FAISS, Pinecone, or Chroma.
- Embedding Models: Convert text into numerical vectors for similarity search and retrieval.
- Context Injection: Add retrieved information into the prompt before generating a response.
- Use Cases: Power chatbots, enterprise search, question answering, and knowledge-based assistants.
RAG enables generative AI systems to deliver more reliable, explainable, and information-grounded responses in production environments.
Step 14: AI Agents and Tool Use
AI agents are systems that can make decisions, take actions, and use external tools to complete tasks automatically. Unlike simple text generation, AI agents can plan steps, retrieve information, and interact with software or services to achieve specific goals. This makes them an important part of modern generative AI systems, especially for complex, multi-step workflows. Below are the key points to learn:
- Task Planning: Learn how agents break high-level goals into smaller tasks, sequence actions, and adjust plans dynamically.
- Tool Integration: Understand how to connect AI models with tools such as search engines, APIs, databases, and external services.
- Function Calling: Enable models to trigger predefined functions to perform actions programmatically.
- Memory Systems: Store past interactions so agents can maintain context across conversations or tasks.
- Use Cases: Build AI assistants, autonomous research agents, automated workflows, and intelligent productivity applications.
Learning AI agents and tool use helps you design intelligent systems that can act autonomously, adapt to new situations, and solve real-world problems effectively.
Read More AI-Related Guides
| Best AI Tools for Content Writing | How to Make Money With AI? |
| Gemini vs. ChatGPT: Which is Better | Perplexity vs ChatGPT: Which is Better |
| How to Use AI for SEO? | Top 7 ChatGPT Alternatives |
Step 15: Deployment of Generative AI Applications
Deployment is the process of making your generative AI model available for real users. After building and testing a model, you need to integrate it into applications so people can interact with it through websites, mobile apps, or APIs. Deployment ensures your AI system runs smoothly, responds quickly, and can handle multiple users reliably. Below are the key points to learn:
- API Development: Expose generative AI models through APIs so applications can securely send requests and receive responses.
- Cloud Platforms: Host models on cloud services such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure for scalability and reliability.
- Containerization: Use Docker to package applications and ensure consistent environments across development and production systems.
- Performance Monitoring: Track response times, errors, and usage to maintain system quality.
- Security and Access Control: Protect your application and manage who can use the AI system.
Learning deployment helps you move from experimentation to real-world AI products that users can access and benefit from.
Step 16: MLOps for Generative AI
MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) focuses on managing, deploying, and maintaining generative AI models in real-world production environments. It ensures that models remain reliable, scalable, and up to date even after deployment. MLOps combines machine learning practices with DevOps principles to automate workflows, improve collaboration, and maintain system performance over time. Below are the key points to learn:
- Model Versioning: Maintain clear records of model updates, improvements, and experiments so teams can compare performance and roll back to stable versions if needed.
- Data Versioning: Track changes in datasets used for training and fine-tuning to ensure experiments are reproducible and results remain consistent.
- CI/CD for ML: Automate testing, validation, and deployment of model updates to release improvements quickly and safely.
- Monitoring & Logging: Continuously track model performance, system health, and errors to quickly detect and resolve issues.
- Model Drift Detection: Identify when model performance drops due to changing data patterns, prompting retraining or updates.
Understanding MLOps helps you manage generative AI systems efficiently and keep them performing well in production.
Step 17: AI Safety and Responsible AI
AI safety and responsible AI focus on building generative AI systems that are ethical, secure, and trustworthy. This step helps ensure AI models produce safe outputs, treat users fairly, and respect privacy while operating reliably in real-world environments.
It also emphasizes reducing bias, improving transparency, protecting sensitive data, and maintaining human oversight over AI decisions. Practicing responsible AI builds user trust, supports legal and ethical compliance, and ensures generative AI technologies are used in a safe, responsible, and sustainable way.

Step 18: Performance Optimization
Performance optimization focuses on making generative AI models run faster, use fewer resources, and respond efficiently in real-world applications. Large models can be computationally expensive, so optimizing them helps reduce costs, improve response times, and make deployment more practical. Efficient models are especially important when serving many users or running on limited hardware.
- Model Quantization: Reduce model size by using lower-precision numbers, which speeds up inference and lowers memory usage.
- Pruning: Remove less important model parameters to make the model lighter and faster without major accuracy loss.
- Batch Processing: Handle multiple requests together to improve system efficiency.
- Hardware Acceleration: Use GPUs, TPUs, or specialized chips to speed up model execution.
- Caching Responses: Store frequent outputs to reduce repeated computation and improve response time.
Learning performance optimization helps you build scalable and cost-effective generative AI systems for production environments.
Step 19: Real-World Generative AI Projects
Working on real-world projects is one of the best ways to strengthen your understanding of generative AI. Projects help you apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios, solve real problems, and build a strong portfolio. By creating end-to-end applications, you learn how different components, models, data, prompts, and deployment come together in a complete system. Below are useful projects that you can build to gain hands-on experience and strengthen your generative AI skills.
- AI Chatbot with Memory: Build a chatbot that remembers past interactions to provide more personalized responses.
- Document Question-Answering System: Create a system that answers questions using information from uploaded documents.
- AI Content Generator: Develop a tool that generates blog posts, summaries, or marketing content.
- Text-to-Image Application: Build an app that generates images based on user text prompts.
- Voice or Speech Assistant: Create a basic voice-based assistant that can respond to spoken queries.
Building these projects prepares you for real industry tasks and helps demonstrate your practical generative AI skills.
Step 20: Building a Generative AI Portfolio
Building a strong generative AI portfolio is essential to showcase your practical skills and creativity. A portfolio highlights the projects you have completed, the tools you have used, and the problems you have solved. It helps employers or clients understand your hands-on experience with models, prompts, data, and deployment.
Include a variety of projects such as chatbots, content generators, document Q&A systems, or image generation apps. Share code on GitHub, write clear project descriptions, and explain the technologies used. A well-presented portfolio demonstrates your ability to apply generative AI in real-world scenarios.
Career Paths After Completing Generative AI
After completing the roadmap of generative AI, you gain practical skills to work with modern AI systems, build real applications, and pursue high-growth career roles across industries using advanced generative technologies.
- Generative AI Engineer: Design, fine-tune, and deploy generative models such as LLMs and diffusion models, build AI-powered applications, optimize prompts, and integrate AI systems into scalable production environments.
- Prompt Engineer: Develop, test, and optimize prompts to guide AI systems toward accurate and useful outputs. Collaborate with developers and product teams to improve response quality, automate workflows, and enhance user interaction with AI tools.
- AI Researcher: Explore new model architectures, training methods, and optimization techniques to advance generative AI capabilities. Conduct experiments, publish findings, and contribute to improving model efficiency, safety, and real-world performance.
- MLOps Engineer: Manage deployment, monitoring, versioning, and lifecycle of AI models, ensure scalability and reliability, automate workflows, and maintain production-grade generative AI systems efficiently.
- Natural language processing (NLP) Engineer: Build and optimize language-based AI systems such as chatbots, translators, and text analytics tools by applying NLP techniques, embeddings, and language models to real-world applications.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Develop, train, and deploy machine learning and deep learning models, handle large datasets, improve model performance, and collaborate with engineering teams to build reliable AI-driven systems.
With the right skills and projects, these opportunities allow you to build a strong career in the rapidly evolving generative AI industry.
Generative AI Market Size and Future Growth
The global generative AI engineering market is growing at an exceptional pace, projected to expand from about USD 21.57 billion in 2024 to USD 29.16 billion in 2025, and expected to reach nearly USD 286.41 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of over 38%. This rapid expansion reflects increasing enterprise investment in generative AI technologies across sectors.
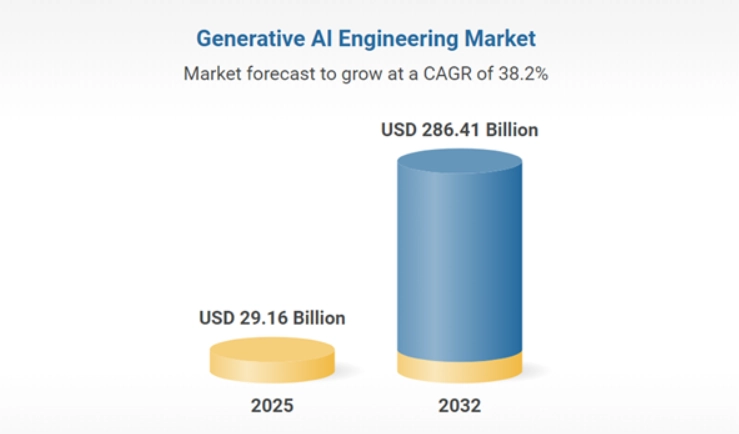
Demand for generative AI professionals continues to rise as companies integrate AI systems, from LLMs to multimodal models, into products and services. Enterprises now seek engineers who can build, fine-tune, deploy, and manage these technologies at scale, creating strong job growth potential worldwide.
Generative AI Engineer Salary in India (2026)
| Experience Level | Average Salary Range |
| Fresher / Entry (0–2 yrs) | ₹10 – ₹16 LPA |
| Mid-Level (2–5 years) | ₹18 – ₹32 LPA |
| Senior (5+ yrs) | ₹35 – ₹55+ LPA |
Note: Salaries vary based on skills, company, and city, with top tech hubs offering premium packages.
Salary Influencing Factors:
- Skills & Experience: Advanced generative AI skills (e.g., prompt engineering, model deployment) command higher salaries.
- Industry & Company Type: Product companies and AI-first startups generally offer higher compensation than traditional IT firms.
- Location: Major tech cities like Bengaluru, Mumbai, and Hyderabad often offer higher pay than smaller regions.
Generative AI roles are in high demand globally as organizations compete for limited talent with deep AI expertise, making upskilling and practical project experience valuable career differentiators.

FAQs About Generative AI Roadmap
You should follow a generative AI roadmap if you are a student, developer, or professional who wants structured learning, hands-on practice, and clear direction to understand models, tools, and applications without feeling overwhelmed during your learning journey.
You do not need advanced coding skills, but you should know basic Python concepts. As you follow the gen ai beginner roadmap, you gradually improve coding through practice, examples, and small projects focused learning, guided steps, consistently.
The time to complete a generative AI roadmap depends on your background and consistency. If you study regularly, you can finish learning core skills, projects, and deployment basics within six to nine months with steady daily practice.
Generative AI may seem complex at first, but it becomes easier when you learn step by step. By following a generative AI roadmap for beginners, you understand concepts through examples, visuals, and guided projects without confusion or stress.
While learning generative AI, you should build projects like chatbots, AI image generators, text summarizers, recommendation tools, and AI assistants because these projects strengthen your skills, confidence, and job-ready portfolio through practical problem-solving, real use cases, exposure.
You do not need a formal degree to become a generative AI Engineer. You can succeed by following a generative AI career roadmap, building projects, learning tools, and proving skills through practical experience with consistent effort, dedication.
Generative AI is a strong career choice because companies invest heavily in AI-powered products. When you follow a generative AI learning roadmap, you prepare yourself for high-demand, future-ready roles across industries with long-term growth, stability, and impact.
A gen AI roadmap helps you stay focused by organizing topics in the right order. You avoid confusion, track progress easily, practice regularly, and build confidence as each step prepares you for the next stage effectively and smoothly.
Explore Our Free Courses




Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Comments (0)
No comments yet.