AI engineering is the field focused on designing, building, and maintaining intelligent systems that can learn from data and make decisions automatically. It combines artificial intelligence concepts with programming, mathematics, and machine learning to create applications such as chatbots, recommendation systems, and predictive models. Because AI engineering includes many tools and technologies, beginners often feel unsure about where to start and what skills to learn first.
This AI engineer roadmap provides a clear and structured learning path to follow. It helps you move step by step from basic programming and math to advanced AI models and real-world projects. By following a roadmap, you avoid confusion, save time, and focus on the skills that matter most for building a successful career in AI engineering.
Who is an AI Engineer?
An AI Engineer is a professional who designs, builds, and deploys intelligent systems that can learn from data and make decisions. This role combines programming, machine learning, and mathematical concepts to develop AI-powered applications.
AI Engineers work with large datasets, train models, and integrate AI solutions into real-world products. They focus on building scalable, efficient, and reliable systems that solve complex problems across various industries.
Key Responsibilities of an AI Engineer
- Design, train, and optimize machine learning and deep learning models to solve real-world problems with high accuracy, efficiency, and scalable performance in production environments.
- Collect, clean, and preprocess structured and unstructured data to ensure high-quality input for training, testing, and validating AI and machine learning models.
- Implement deep learning and natural language processing techniques to build applications such as chatbots, image recognition systems, and language-based AI tools.
- Deploy AI models into applications using APIs, containers, and automation tools, ensuring models run smoothly, scale effectively, and remain maintainable over time.
- Monitor model behavior, track performance metrics, and regularly update models to handle data changes, reduce errors, and maintain consistent output quality in production systems.
Why Follow an AI Engineer Roadmap?
Following an AI Engineer roadmap gives clear direction, saves time, and helps you learn skills in the right order. It removes confusion, keeps learning focused, and prepares you for real-world AI roles with confidence and practical knowledge. Below are the key reasons to follow a structured roadmap.
- Clear Learning Path: A roadmap shows exactly what to learn and when to learn it, helping you progress from basic concepts to advanced AI topics without missing important skills or wasting effort.
- Better Skill Focus: It helps you focus on industry-relevant tools, technologies, and concepts, so your learning aligns with real job requirements instead of scattered or outdated information.
- Career-Oriented Growth: By following a roadmap, you build job-ready skills, create meaningful projects, and prepare effectively for interviews, making it easier to enter and grow in AI engineering roles.
In short, a roadmap keeps learning structured, practical, and aligned with long-term career success in AI engineering.
Recommended Professional Certificates
Full Stack Development Mentorship Program
WordPress Bootcamp
AI Engineer Roadmap: Step-by-Step Learning Guide
This roadmap outlines a clear and structured approach to becoming anAI engineer in 2026. It helps learners move logically from basic skills to advanced AI concepts without confusion. By following this roadmap for AI engineers, beginners and professionals can stay focused, avoid random learning, and build job-ready skills step by step. Below are the learning steps to follow:
- Build Strong Programming Foundations
- Learn Mathematics Required for AI
- Understand Data Handling and Data Processing
- Master Machine Learning Fundamentals
- Learn Deep Learning and Neural Networks
- Work with AI Frameworks and Libraries
- Understand Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Learn Computer Vision Concepts
- Explore Generative AI and Large Language Models
- Deploy AI Models and Learn MLOps Basics
- Work with Cloud Platforms and AI Infrastructure
- Build Real-World AI Projects and Portfolio
- Prepare for Jobs, Interviews, and Career Growth
Now, we will learn each step in detail, explaining what to learn, why it matters, and how it helps you progress from beginner level to a confident, job-ready AI engineer with practical skills.
Step 1: Build Strong Programming Foundations
Building strong programming foundations is the first and most important step in becoming an AI Engineer. Programming helps you write logic, handle data, and implement machine learning models correctly. Python is the most widely used language in AI because it is simple, readable, and supported by powerful AI libraries.
At this stage, focus on learning the basics of Python, including variables, data types, loops, functions, and conditional statements. You should also understand lists, dictionaries, sets, tuples, and basic file handling. Along with this, learn core data structure concepts such as arrays, stacks, queues, linked lists, and basic trees to manage data efficiently.
You can learn more about Python from basic to advanced through our Python tutorial. It provides structured lessons, clear explanations, and practical examples that help you build strong Python skills and move confidently toward becoming an AI Engineer.
Step 2: Learn the Mathematics Required for AI
Mathematics forms the core of artificial intelligence and explains how AI models learn from data and improve over time. Understanding mathematical concepts helps you interpret algorithms, tune models, and make informed decisions while building efficient and accurate AI systems.
- Linear Algebra: Vectors, matrices, matrix operations, eigenvalues, eigenvectors, dot product, and matrix multiplication.
- Probability: Random variables, probability distributions, conditional probability, Bayes’ theorem, and expectation.
- Statistics: Mean, median, variance, standard deviation, data distribution, correlation, and hypothesis testing.
- Calculus: Derivatives, partial derivatives, gradients, chain rule, and optimization basics.
- Optimization Techniques: Cost functions, gradient descent, learning rate, and convergence concepts.
A clear understanding of these topics makes complex AI models easier to grasp. Strong mathematical skills improve model performance, reduce errors, and help you debug issues effectively while working on real-world AI and machine learning projects.
Step 3: Understand Data Handling and Data Processing
Data handling and data processing are essential skills for an AI Engineer because AI models depend heavily on data quality. Learning how to collect, clean, transform, and organize data ensures accurate model training and meaningful results. This step focuses on converting raw data into a usable format for analysis and machine learning.
- Data Collection: Structured and unstructured data sources, APIs, databases, web scraping basics, and common data formats such as CSV, JSON, and Excel.
- Data Cleaning: Handle missing values, remove duplicates, correct inconsistent entries, manage outliers, and fix data errors to improve overall data quality and reliability.
- Data Transformation: Apply normalization, standardization, feature scaling, encoding of categorical variables, and feature extraction to convert raw data into model-ready formats.
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): Analyze data distributions, identify trends and patterns, detect anomalies, and use visualizations to understand data behavior before training models.
- Data Processing Tools: Pandas, NumPy, basic SQL queries, and essential data manipulation techniques.
Strong data-handling skills help you build better AI models by providing clean and meaningful data. Mastering this step reduces errors, improves accuracy, and prepares you for advanced machine learning and deep learning tasks.

Step 4: Master Machine Learning Fundamentals
Machine learning plays a major role in AI systems and focuses on enabling models to learn patterns from data. In this step, you understand how data is converted into models, how algorithms find relationships, and how predictions are generated. These fundamentals help you build systems that improve automatically with experience.
Learning machine learning basics also helps you understand model behavior and performance. You gain clarity on choosing the right algorithm, training models correctly, and reducing errors. Strong fundamentals make it easier to solve real-world problems and prepare you for advanced AI concepts.
- Types of Machine Learning: Supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning, and reinforcement learning
- Common Algorithms: Linear regression, logistic regression, decision trees, random forests, k-nearest neighbors, and support vector machines
- Model Training: Train-test split, cross-validation, and hyperparameter tuning
- Model Evaluation: Accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, confusion matrix, and ROC curve
- Common Challenges: Overfitting, underfitting, bias, variance, and data leakage
Mastering machine learning fundamentals prepares you for deep learning, advanced AI models, and real-world problem-solving with confidence and clarity.
Step 5: Learn Deep Learning and Neural Networks
Deep learning focuses on training multi-layered neural networks to process large and complex datasets. It is commonly applied in areas such as image analysis, language understanding, voice recognition, and video processing. By learning patterns directly from raw data, deep learning models help AI systems deliver precise and effective results in practical applications.
In the above diagram, you can see how a neural network is designed and trained. Data enters through the input layer, where features are provided to the model. The hidden layers process this data using weights, biases, and activation functions to learn patterns. Finally, the output layer produces predictions or classifications based on learned information. During training, errors are calculated and weights are updated to improve accuracy.
You also explore different types of deep learning architectures. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are used for image and vision tasks, while Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and their variants handle sequential data like text and time series. Mastering deep learning prepares you to build powerful, scalable, and intelligent AI systems used in real-world production environments.
Step 6: Work with AI Frameworks and Libraries
AI frameworks and libraries help AI engineers build, train, and deploy models efficiently without implementing algorithms from scratch. These tools simplify data processing, model development, and experimentation, allowing you to focus on solving problems and improving performance. Mastering them is essential for developing scalable and production-ready AI applications.
- NumPy: Provides powerful support for numerical computing, array operations, and mathematical calculations. It forms the foundation for data processing, linear algebra operations, and efficient computation in AI and machine learning workflows.
- Pandas: Used for data manipulation and analysis. It helps clean, transform, filter, and organize large datasets, making raw data suitable for machine learning and AI model training.
- Matplotlib and Seaborn: Used for data visualization. These libraries help you understand data distributions, detect patterns, identify outliers, and analyze model performance using clear and informative charts.
- Scikit-learn: Offers simple and efficient tools for machine learning algorithms, preprocessing, model training, evaluation, and hyperparameter tuning for classical machine learning tasks.
- TensorFlow and Keras: Used to build, train, and deploy deep learning models. They support neural networks, large datasets, and scalable production-level AI systems.
- PyTorch: Commonly used for deep learning research and production. It offers flexibility, dynamic computation graphs, and easier debugging, making it popular for advanced AI model development.
Learning these frameworks makes AI development faster and more reliable. Strong hands-on practice with these tools prepares you to build real-world AI systems, handle large datasets, and move confidently toward advanced AI applications and deployment.
Upcoming Masterclass
Attend our live classes led by experienced and desiccated instructors of Wscube Tech.
Step 7: Understand Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It plays a key role in AI applications such as chatbots, search engines, voice assistants, and text analysis systems. Learning NLP helps AI engineers build models that effectively work with text and speech data.
NLP focuses on converting unstructured text into meaningful information that machines can process. This step teaches you how language data is cleaned, represented, and used to train intelligent models for real-world applications.
- Text Preprocessing: Tokenization, stop-word removal, stemming, lemmatization, handling punctuation, and converting text into machine-readable formats.
- Text Representation: Bag of Words, TF-IDF, word embeddings, and sentence embeddings to convert text into numerical form for machine learning models.
- Core NLP Tasks: Text classification, sentiment analysis, named entity recognition (NER), text summarization, and language translation.
- NLP Models and Techniques: Traditional models, basic neural networks, sequence models, and an introduction to transformer-based approaches.
- Popular NLP Libraries: NLTK, SpaCy, Hugging Face Transformers, and NLP tools available in Python.
Understanding NLP prepares you to work on language-based AI systems. It builds the foundation for advanced areas such as conversational AI, large language models, and generative AI applications used across industries.
Step 8: Learn Computer Vision Concepts
Computer Vision allows machines to understand and interpret visual information from images and videos. It is a core AI skill used in applications such as medical imaging, self-driving cars, object detection, facial recognition, and surveillance systems. Learning computer vision helps AI engineers build models that can analyze, identify, and extract meaningful information from visual data.
This step focuses on how images are represented, processed, and used to train intelligent models. You learn to convert raw visual data into features that AI systems can understand and use for predictions.
- Image Basics: Pixels, image resolution, color spaces (RGB, grayscale), image formats, and basic image transformations.
- Image Processing Techniques: Filtering, edge detection, thresholding, resizing, normalization, and noise reduction.
- Core Computer Vision Tasks: Image classification, object detection, image segmentation, and face recognition.
- Deep Learning for Vision: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), feature maps, pooling layers, and transfer learning concepts.
- Computer Vision Libraries: OpenCV, TensorFlow, PyTorch, and image-processing tools available in Python.
Learning computer vision equips you to build AI systems that can “see” and understand the world. These skills are essential for advanced AI applications involving images, videos, and real-time visual data processing.
Step 9: Explore Generative AI and Large Language Models
Generative AI focuses on creating new content such as text, images, code, and audio by learning patterns from large datasets. It represents a shift from traditional prediction-based AI to systems capable of producing creative and meaningful outputs. These technologies are widely used in chatbots, virtual assistants, content creation tools, and automated support systems.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are a key part of generative AI and are trained on massive amounts of text data. In this step, you learn how these models generate human-like responses, how prompts influence outputs, and how generative AI is applied in real-world products. Understanding this area prepares you to build intelligent, interactive, and scalable AI-driven applications.
Explore More Career Guides
Step 10: Deploy AI Models and Learn MLOps Basics
Deploying AI models means making trained models available for real-world applications. This process involves saving models, loading them into applications, and serving predictions through APIs or services. Proper deployment ensures models work efficiently, scale with demand, and deliver consistent results outside the development environment.
MLOps is very important for managing AI models after deployment. It focuses on maintaining model performance, automating workflows, and ensuring smooth collaboration between teams. MLOps helps keep AI systems stable, updated, and reliable over time.
MLOps Basics
- Model Versioning: Track different model versions, experiments, and updates to manage changes and improvements over time.
- Model Monitoring: Monitor model performance, data drift, and prediction quality after deployment to detect issues early.
- Automation and CI/CD: Automate model training, testing, and deployment using CI/CD pipelines to reduce errors and speed up updates.
- Model Retraining: Retrain models regularly using new data to maintain accuracy and adapt to changing data patterns.
- Collaboration and Workflow Management: Improve collaboration between data science and engineering teams by using standardized tools and workflows.
Learning deployment and MLOps basics helps you build production-ready AI systems that are stable, scalable, and easier to maintain in real-world environments.
Step 11: Work with Cloud Platforms and AI Infrastructure
Cloud platforms provide the computing power, storage, and tools required to build, train, deploy, and scale AI models efficiently. Cloud-based learning and AI infrastructure help AI engineers handle large datasets, run models faster, and deploy reliable AI systems.
- Cloud Service Providers: Learn how platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure support AI workloads, model deployment, and scalable infrastructure.
- Compute Resources: Understand CPUs, GPUs, and TPUs, and how to choose the right resources for training and inference tasks.
- Storage and Data Management: Work with cloud storage services to store, manage, and access large datasets securely and efficiently.
- Model Deployment on Cloud: Deploy AI models using cloud services, APIs, and managed machine learning platforms.
- Scalability and Cost Management: Learn how to scale AI applications based on demand while optimizing performance and controlling cloud costs.
Working with cloud platforms and AI infrastructure prepares you to build production-ready, scalable, and cost-efficient AI systems used in real-world industry applications.
Step 12: Build Real-World AI Projects and Portfolio
Building real-world AI projects is essential for turning theoretical knowledge into practical skills. Projects help you understand how AI systems work from end to end, including data collection, model training, evaluation, and deployment. They strengthen problem-solving abilities and show how well you can apply AI concepts to real situations.
Creating strong portfolio allows you to showcase your skills through meaningful projects such as prediction systems, chatbots, recommendation engines, or image classification models. A well-documented portfolio builds confidence, highlights hands-on experience, and greatly improves your chances of securing AI roles, internships, or project opportunities.

Step 13: Prepare for Jobs, Interviews, and Career Growth
Preparing for jobs and interviews is the final step toward building a successful AI career. This stage focuses on strengthening problem-solving skills, revising core concepts, and gaining confidence in explaining projects and technical decisions. Interview preparation helps you present your knowledge clearly and handle real-world scenarios effectively.
Following an AI engineer roadmap also means planning long-term career growth. This includes improving your resume, building strong project explanations, staying updated with new AI trends, and continuously learning advanced tools. Consistent preparation helps you secure roles, grow professionally, and adapt to the evolving AI industry.
Career Opportunities After Learning AI Engineering
Learning AI engineering opens doors to many high-growth technology roles across industries. Below are some career options you can pursue after learning AI.
- AI Engineer: Works on designing, building, and deploying intelligent systems that learn from data. This role focuses on model development, optimization, and integrating AI solutions into real-world applications.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Specializes in developing, training, and improving machine learning models. This role focuses on scalable pipelines, model performance, and turning ML experiments into production-ready systems.
- Data Scientist: Uses data analysis, statistics, and machine learning to extract insights from data. This role focuses on problem-solving, predictive modeling, and supporting business decisions using data-driven approaches.
- MLOps Engineer: Focuses on deploying, monitoring, and maintaining machine learning models in production. This role ensures automation, scalability, and long-term performance of AI systems in real environments.
Overall, AI engineering offers strong career growth, competitive salaries, and opportunities to work on impactful technologies shaping the future across healthcare, finance, education, and many other industries.
AI Engineer Salary and Demand (2026)
The Artificial Intelligence Engineering Market is growing rapidly worldwide. The global AI engineering market was valued at around USD 12.65 billion in 2024 and is projected to expand to about USD 281.47 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 36.37% from 2025 to 2034. This growth shows a strong demand for AI technologies, tools, and skilled professionals in many industries like IT, healthcare, automotive, and finance.
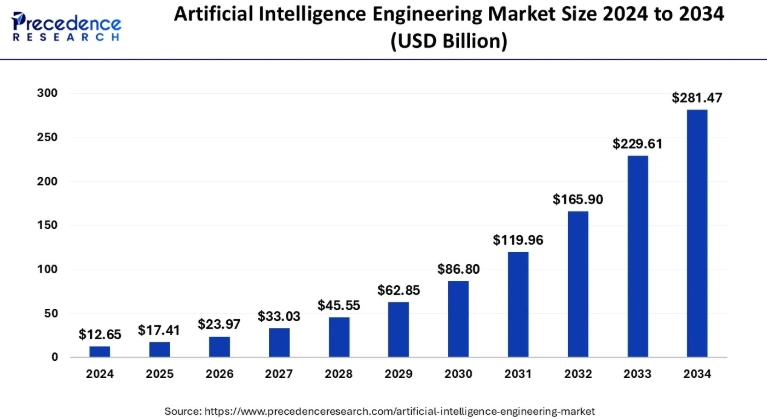
In India, companies are increasingly adopting AI solutions, creating more opportunities for AI engineers who can build, deploy, and optimize intelligent systems. Skills in machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, cloud platforms, and software development are highly valuable. The expanding use of AI technologies means professionals with these skills are in high demand across startups, tech firms, and global enterprises.
AI Engineer Salary in India (2026)
| Experience Level | Average Salary Range |
| Fresher (0–2 years) | 11.1 LPA – ₹12.3 LPA |
| Mid-Level (2–5 years) | ₹18.8 LPA – ₹21.8 LPA |
| Experienced (5+ years) | ₹21.1 LPA – ₹27.3+ LPA |
Salary ranges can vary with skills, company size, location, and projects you work on.
With rapid market growth, increasing adoption of AI tools, and strong industry demand, a career as an AI engineer in India offers excellent opportunities and future stability.
AI Engineer Roadmap (Video Guide)

FAQs About AI Engineer Roadmap
An AI Engineer roadmap is a step-by-step learning path that shows what skills you should learn and in what order. It helps you move from programming basics to machine learning, deep learning, deployment, and real-world AI projects.
Yes, the ai engineer roadmap for beginners is designed to start from scratch. You begin with Python and basic math, then slowly move toward machine learning, deep learning, and deployment without feeling overwhelmed or confused.
If you study consistently, you can cover the roadmap for AI engineer in 9–12 months. Your speed depends on learning time, practice, and project work. Regular hands-on practice helps you progress faster and retain concepts better.
You do not need advanced coding skills, but basic programming is important. The AI engineer roadmap from scratch starts with Python basics, helping you build logic, handle data, and gradually move toward machine learning and AI model development.
Python is the best choice for AI engineering. Most AI engineering roadmap guides start with Python because it is easy to learn, widely used, and supported by powerful libraries for machine learning, deep learning, and data processing.
Yes, math is important, but you do not need to be a math expert. You should understand basics of linear algebra, probability, and calculus. These help you understand how models learn and how to improve performance.
Yes, the AI engineer roadmap for freshers is very helpful. It focuses on building fundamentals, practical skills, and projects. With consistent learning and practice, you can become job-ready even without prior industry experience.
Projects are extremely important. When you follow an AI roadmap for beginners, projects help you apply theory, understand real-world problems, and build a strong portfolio that shows employers what you can actually build.
Yes, a good roadmap to ai engineer includes interview preparation, problem-solving practice, and portfolio building. It helps you understand industry expectations and prepares you for technical interviews and real-world AI engineering roles.
Yes, you can become an AI engineer without a formal degree. By following a clear AI engineer roadmap, learning core skills, building real-world projects, and gaining hands-on experience, you can prove your abilities and access strong career opportunities in the AI field.
Free Courses for You



Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Comments (0)
No comments yet.